|
Appendix A. ICAO FLIGHT PLANS
1. ICAO
Model Flight Plan Form.
2.
Instructions for the Completion of the Flight Plan Form.
3.
Instructions for the Transmission of a Filed Flight Plan (FPL) Message.
4.
Instructions for the Transmission of a Supplementary Flight Plan (SPL)
Message.
5.
Example of Completed Flight Plan Form.
6. ICAO
Model Flight Plan, Reverse Side.
7. ICAO
Model Repetitive Flight Plan (RPL) Listing Form.
8.
Example of a Completed Repetitive Flight Plan (RPL) Listing Form.
1. ICAO Model Flight Plan Form
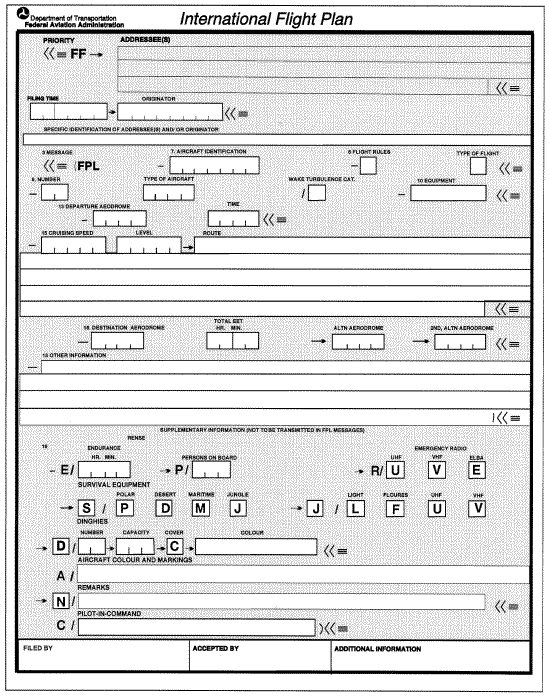
2. Instructions for the Completion
of the Flight Plan Form
2.1
General
Follow the prescribed formats and manner of specifying data.
Start entering data in the first space provided. Leave unused spaces blank.
ENTER all clock times in
4 figures UTC.
ENTER all estimated elapsed times in 4 figures (hours and minutes).
Shaded area preceding Item 3 to be completed by ATS and COM services, unless the responsibility for originating flight
plan messages has been delegated.
NOTE
The term “aerodrome,” where used in the flight plan, also covers sites other than aerodromes which may be used by
certain types of aircraft; for example, helicopters or balloons.
2.2 Instructions for entering ATS data
Complete Items 7 to 18 as indicated below.
Complete also Item 19 as indicated below, when required by the appropriate ATS authority or when otherwise deemed
necessary.
NOTE
1. Item numbers on the form are not consecutive, as they correspond to Field Type numbers in ATS messages.
2. ATS data systems may impose communications or processing constraints on information in filed flight plans. Possible
constraints may, for example, be limits regarding item length, number of elements in the route item, or total flight plan
length. Significant constraints are documented in the relevant Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP).
ITEM 7: AIRCRAFT IDENTIFICATION (MAXIMUM 7 CHARACTERS)
ENTER one of the following aircraft identifications, not exceeding 7 alphanumeric characters and without hyphens or
symbols:
(a) The ICAO designator for the aircraft operating agency, followed by the flight identification (for example,
KLM511, NGA213, JTR25). When in radiotelephony the call sign to be used by the aircraft will consist of
the ICAO telephony designator for the operating agency followed by the flight identification (for example,
KLM511, NIGERIA213, JESTER25);
(b)
The nationality or common mark and registration marking of the aircraft (for example, EIAKO, 4XBCD,
N2567GA), when:
(1) In radiotelephony, the call sign to be used by the aircraft will consist of this identification alone (for
example, CGAJS) or preceded by the ICAO telephony designator for the aircraft operating agency
(for example, BLIZZARD CGAJS); or
(2) The aircraft is not equipped with radio.
NOTE
1. Standards for nationality, common and registration marks to be used are contained in Annex 7, Chapter 2.
2. Provisions for using radiotelephony call signs are contained in Annex 10, Volume II, Chapter 5. ICAO designators and
telephony designators for aircraft operating agencies are contained in Doc 8585 — Designators for Aircraft Operating
Agencies, Aeronautical Authorities and Services.
ITEM 8: FLIGHT RULES AND TYPE OF FLIGHT (1 OR 2 CHARACTERS)
Flight Rules
ENTER one of the following letters to denote the category of flight rules with which the pilot intends to comply:
I if it is intended that the entire flight will be operated under IFR.
V if it is intended that the entire flight will be operated under VFR.
Y if the flight initially will be operated under IFR, followed by one or more changes of flight rules.
Z if the flight initially will be operated under VFR, followed by one or more changes of flight rules.
NOTE
U.S. domestic automation systems cannot accept a flight plan that begins under VFR and subsequently changes to one
or more flight rules (that is, “Z”). For this purpose, file separate flight plans for the portions of the route that the pilot
intends to conduct under IFR.
Specify in Item 15 the point or points where change of flight rules is planned.
Type of flight
ENTER one of the following letters to denote the type of flight when required by the appropriate ATS authority:
S if scheduled air service
N if nonscheduled air transport operation
G if general aviation
M if military
X if other than any of the defined categories above.
Specify flight status following the indicator “STS” in Item 18, or when necessary to denote other reasons for specific
handling by ATS, indicate the reason following the indicator “RMK” in Item 18.
ITEM 9: NUMBER AND TYPE OF AIRCRAFT AND WAKE TURBULENCE CATEGORY
Number of aircraft (1 or 2 characters)
ENTER the number of aircraft, if more than one.
Type of aircraft (2 to 4 characters)
ENTER the appropriate designator as specified in ICAO Doc 8643, Aircraft Type Designators,
OR
if no such designator has been assigned, or in case of formation flights comprising more than one type,
ENTER ZZZZ, and
SPECIFY in Item 18, the (numbers and) type(s) of aircraft preceded by TYP/.
Wake turbulence category (1 character)
ENTER an oblique stroke followed by one of the following letters to indicate the wake turbulence category of the aircraft:
H HEAVY, to indicate an aircraft type with a maximum certificated takeoff mass of 136 000 kg or more;
M MEDIUM, to indicate an aircraft type with a maximum certificated takeoff mass of less than 136,000 kg but more than 7,000 kg;
L LIGHT, to indicate an aircraft type with a maximum certificated takeoff mass of 7,000 kg or less.
ITEM 10: EQUIPMENT AND CAPABILITIES
Capabilities comprise the following elements:
(a) Presence of relevant serviceable equipment on board the aircraft;
(b) Equipment and capabilities commensurate with flight crew qualifications; and
(c) Where applicable, authorization from the appropriate authority.
Radio communication, navigation and approach aid equipment and capabilities
ENTER one letter as follows:
N if no COM/NAV/approach aid equipment for the route to be flown is carried, or the equipment is unserviceable,
OR
S if standard COM/NAV/approach aid equipment for the route to be flown is carried and serviceable (see Note 1),
AND/OR
ENTER one or more of the following letters to indicate the serviceable COM/NAV/ approach aid equipment and capabilities available:
A GBAS landing system
B LPV (APV with SBAS)
C LORAN C
D DME
E1 FMC WPR ACARS
E2 DFIS ACARS
E3 PDC ACARS
F ADF
G GNSS (See Note 2)
H HF RTF
I Intertial Navigation
J1 CPDLC ATN VDL Mode 2 (See Note 3)
J2 CPDLC FANS 1/A HFDL
J3 CPDLC FANS 1/A VDL Mode A
J4 CPDLC FANS 1/A VDL Mode 2
J5 CPDLC FANS 1/A SATCOM(INMARSAT)
J6 CPDLC FANS 1/A SATCOM (MTSAT)
J7 CPDLC FANS 1/A SATCOM (Iridium)
K MLS
L ILS
M1 ATC RTF SATCOM (INMARSAT)
M2 ATC RTF (MTSAT)
M3 ATC RTF (Iridium)
O VOR P1–P9 Reserved for RCP
R PBN approved (See Note 4)
T TACAN
U UHF RTF
V VHF RTF
W RVSM approved
X MNPS approved
Y VHF with 8.33 kHz channel spacing capability
Z Other equipment carried or other capabilities (See Note 5)
Any alphanumeric characters not indicated above are reserved.
NOTE
1. If the letter S is used, standard equipment is considered to be VHF RTF, VOR, and ILS, unless another combination is
prescribed by the appropriate ATS authority.
2. If the letter G is used, the types of external GNSS augmentation, if any, are specified in Item 18 following the indicator
NAV/ and separated by a space.
3. See RTCA/EUROCAE Interoperability Requirements Standard For ATN Baseline 1 (ATN B1 INTEROP Standard –
DO280B/ED110B) for data link services air traffic control clearance and information/air traffic control
communications management/air traffic control microphone check.
4. If the letter R is used, the performance based navigation levels that can be met are specified in Item 18 following the
indicator PBN/. Guidance material on the application of performance based navigation to a specific route segment, route
or area is contained in the PerformanceBased Navigation Manual (Doc 9613).
5. If the letter Z is used, specify in Item 18 the other equipment carried or other capabilities, preceded by COM/, NAV/
and/or DAT/, as appropriate.
6. Information on navigation capability is provided to ATC for clearance and routing purposes.
Surveillance equipment and capabilities
ENTER N if no surveillance equipment for the route to be flown is carried, or the equipment is unserviceable,
OR
ENTER one or more of the following descriptors, up to a maximum of 20 characters, to describe the serviceable surveillance equipment and/or capabilities on board. Enter no more than one transponder code (Modes A, C, or S)
SSR Modes A and C:
A Transponder Mode A (4 digits 4096 codes)
C Transponder Mode A (4 digits 4096 codes) and Mode C
SSR Mode S:
E Transponder Mode S, including aircraft identification, pressurealtitude and extended squitter (ADSB) capability
H Transponder Mode S, including aircraft identification, pressurealtitude and enhanced surveillance capability
I Transponder Mode S, including aircraft identification, but no pressurealtitude capability
L Transponder Mode S, including aircraft identification, pressurealtitude, extended squitter (ADS-B) and enhanced surveillance capability
P Transponder — Mode S, including pressurealtitude, but no aircraft identification capability
S Transponder Mode S, including both pressurealtitude and aircraft identification capability
X Transponder Mode S with neither aircraft identification nor pressurealtitude capability
NOTE
Enhanced surveillance capability is the ability of the aircraft to downlink aircraft derived data via a Mode S transponder.
ADSB:
B1 ADSB with dedicated 1090 MHz ADSB “out” capability
B2 ADBB with dedicated 1090 MHz ADSB “out” and “in” capability
U1 ADSB “out” capability using UAT
U2 ADSB “out” and “in” capability using UAT
V1 ADSB “out” capability using VDL Mode 4
V2 ADSB “out” and “in” capability using VDL Mode 4
NOTE-
File no more than one code for each type of capability, e.g. file B1 or B2 and not both
ADSC:
D1 ADSC with FANS 1/A capabilities
G1 ADSC with ATN capabilities
Alphanumeric characters not indicated above are reserved.
EXAMPLE
ADE3RV/HB2U2V2G1
NOTE
Additional surveillance application should be listed in Item 18 following the indicator SUR/.
ITEM 13: DEPARTURE AERODROME AND TIME (8 CHARACTERS)
ENTER the ICAO fourletter location indicator of the departure aerodrome as specified in Doc 7910, Location Indicators,
OR
if no location indicator has been assigned,
ENTER ZZZZ and
SPECIFY, in Item 18, the name and location of the aerodrome preceded by DEP/,
OR the first point of the route or the marker radio beacon preceded by DEP/…, if the aircraft has not taken off from the aerodrome,
OR if the flight plan is received from an aircraft in flight,
ENTER AFIL, and
SPECIFY, in Item 18, the ICAO fourletter location indicator of the location of the ATS unit from which supplementary flight plan data can be obtained, preceded by DEP/.
THEN, WITHOUT A SPACE,
ENTER for a flight plan submitted before departure, the estimated offblock time (EOBT),
OR for a flight plan received from an aircraft in flight, the actual or estimated time over the first point of the route to which the flight plan applies.
ITEM 15: ROUTE
ENTER the first cruising speed as in (a) and the first cruising level as in (b), without a space between them.
THEN following the arrow,
ENTER the route description as in (c).
(a) Cruising speed (maximum 5 characters)
ENTER the
True Air Speed for the first or the whole cruising portion of the flight, in terms of:
Kilometers per hour, expressed as K followed by 4 figures (for example, K0830),
or
Knots, expressed as N followed by 4 figures (for example, N0485),
or
True Mach number, when so prescribed by the appropriate ATS authority, to the nearest hundredth of unit Mach, expressed as M followed by 3 figures (for example, M082).
(b) Cruising level (maximum 5 characters)
ENTER the planned cruising level for the first or the whole portion of the route to be flown, in terms of:
Flight level, expressed as F followed by 3 figures (for example, F085; F330), or
*Standard Metric Level in tens of meters, expressed as S followed by 4 figures (for example, S1130), or
Altitude in hundreds of feet, expressed as A followed by 3 figures (for example, A045; A100), or
Altitude in tens of meters, expressed as M followed by 4 figures (for example, M0840), or
for uncontrolled VFR flights, the letters VFR.
*When so prescribed by the appropriate ATS authorities.
(c) Route (including changes of speed, level and/or flight rules)
Flights along designated ATS routes
ENTER if the departure aerodrome is located on or connected to the ATS route, the designator of the first ATS route,
OR if the departure aerodrome is not located on or connected to the ATS route, the letters DCT followed by the point of joining the first ATS route, followed by the designator of the ATS route.
THEN
ENTER each point at which either a change of speed and/or level is planned to start, or a change of ATS route, and/or a change of flight rules is planned,
NOTE
When a transition is planned between a lower and upper ATS route and the routes are oriented in the same direction, the
point of transition does not need to be entered.
FOLLOWED IN EACH CASE
by the designator of the next ATS route segment, even if the same as the previous one,
OR by DCT, if the flight to the next point will be outside a designated route, unless both points are defined by geographical coordinates.
Flights outside designated ATS routes
ENTER points normally not more than 30 minutes flying time or 370 km (200 NM) apart, including each point at which a change of speed or level, a change of track, or a change of flight rules is planned,
OR when required by appropriate ATS authority(ies),
DEFINE the track of flights operating predominantly in an eastwest direction between 70°N and 70°S by reference
to significant points formed by the intersections of half or whole degrees of latitude with meridians spaced at intervals
of 10 degrees of longitude. For flights operating in areas outside those latitudes the tracks must be defined by significant
points formed by the intersection of parallels of latitude with meridians normally spaced at 20 degrees of longitude. The
distance between significant points must, as far as possible, not exceed one hour's flight time. Additional significant points
must be established as deemed necessary.
For flights operating predominantly in a northsouth direction, define tracks by reference to significant points
formed by the intersection of whole degrees of longitude with specified parallels of latitude which are spaced at 5 degrees.
ENTER DCT between successive points unless both points are defined by geographical coordinates or by bearing and
distance.
USE ONLY the conventions in (1) to (5) below and
SEPARATE each subitem by a space.
(1) ATS route (2 to 7 characters)
The coded designator assigned to the route or route segment including, where appropriate, the coded
designator assigned to the standard departure or arrival route (for example, V218, J3, Q108, T111, BCN1, ANC4, AR3,
Bl, R14, UB10, UJ5, UQ104, KODAP2A, RIIVR2).
NOTE
Provisions for the application of route designators are contained in Annex 11, Appendix 1.
(2) Significant point (2 to 11 characters)
The coded designator (2 to 5 characters) assigned to the point (for example, LN, MAY, HADDY), or, if no
coded designator has been assigned, one of the following ways:
Degrees only (7 characters):
2 figures describing latitude in degrees, followed by “N” (North) or “S” (South), followed by 3 figures
describing longitude in degrees, followed by “E” (East) or “W” (West). Make up the correct number of figures, where
necessary, by insertion of zeros, for example, 46N078W.
Degrees and minutes (11 characters):
4 figures describing latitude in degrees and tens and units of minutes followed by “N” (North) or “S” (South),
followed by 5 figures describing longitude in degrees and tens and units of minutes, followed by “E” (East) or “W” (West).
Make up the correct number of figures, where necessary, by entering zeros; for example, 4620N07805W.
Bearing and distance from a significant point:
The identification of the significant point, followed by the bearing from the point in the form of 3 figures
giving degrees magnetic, followed by the distance from the point in the form of 3 figures expressing nautical miles. In
areas of high latitude where it is determined by the appropriate authority that reference to degrees magnetic is impractical,
degrees true may be used. Make up the correct number of figures, where necessary, by insertion of zeros; for example,
a point 180°magnetic at a distance of 40 nautical miles from VOR “DUB” should be expressed as DUB180040.
(3) Change of speed or level (maximum 21 characters)
The point at which a change of speed (5% TAS or 0.01 Mach or more) or a change of level is planned to start,
expressed exactly as in (2) above, followed by an oblique stroke and both the cruising speed and the cruising level,
expressed exactly as in (a) and (b) above, without a space between them,
even when only one of these quantities will be
changed.
EXAMPLES
LN/N0284A045
MAY/N0305Fl80
HADDY/N0420F330
4602N07805W/N0500F350
46N078W/M082F330
DUB180040/N0350M0840
(4) Change of flight rules (maximum 3 characters)
The point
at which the change of flight rules is planned, expressed exactly as in (2) or (3) above as appropriate,
followed by a space and one of the following:
VFR if from IFR to VFR
IFR if from VFR to IFR
EXAMPLES
LN VFR
LN/N0284A050 IFR
NOTE
U.S. domestic automation systems cannot accept flight plans that begin VFR and change to IFR. For this purpose, file
a separate flight plan for the IFR portion of the flight.
(5) Cruise climb (maximum 28 characters)
NOTE
Flight plans containing a cruise climb cannot be accepted by domestic U.S. automation systems.
The letter C followed by an
oblique stroke;
THEN the point at which cruise climb is planned to start, expressed
exactly as in (2) above, followed by an oblique stroke;
THEN
the speed to be maintained during cruise climb, expressed exactly as in (a) above, followed by
the two levels
defining the layer to be occupied during cruise climb, each level expressed exactly as in (b) above,
or the level above which
cruise climb is planned followed by the letters PLUS, without a space between them.
EXAMPLES
C/48N050W/M082F290F350
C/48N050W/M082F290PLUS
C/52N050W/M220F580F620
ITEM 16: DESTINATION AERODROME AND TOTAL ESTIMATED ELAPSED TIME, DESTINATION
ALTERNATE AERODROME(S)
Destination aerodrome and total estimated elapsed time (8 characters)
ENTER the ICAO fourletter location indicator of the destination aerodrome as specified in Doc 7910, Location Indicators,
OR if no location indicator has been assigned,
ENTER ZZZZ followed, without a space, by the total estimated elapsed time, and
SPECIFY in Item 18 the name and location of the aerodrome, preceded by DEST/.
THEN, WITHOUT A SPACE,
ENTER the total estimated elapsed time.
NOTE
For a flight plan received from an aircraft in flight, the total estimated elapsed time is the estimated time from the first
point of the route to which the flight plan applies to the termination point of the flight plan.
Destination alternate aerodrome(s)
ENTER the ICAO fourletter location indicator(s) of not more than two destination alternate aerodromes, as specified in Doc 7910, Location Indicators, separated by a space,
OR if no location indicator has been assigned to the destination alternate aerodrome(s),
ENTER ZZZZ and SPECIFY in Item 18 the name and location of the destination alternate aerodrome(s), preceded by ALTN/.
ITEM 18: OTHER INFORMATION
NOTE
Use of indicators not included under this item may result in data being rejected, processed incorrectly or lost.
Hyphens or oblique strokes should only be used as prescribed below.
ENTER 0 (zero) if no other information,
OR any other necessary information in the sequence shown hereunder, in the form of the appropriate indicator
selected from those defined hereunder followed by an oblique stroke and the information to be recorded:
STS/ Reason for special handling by ATS (for example, a search and rescue mission), as follows:
NOTE
Additional information, if needed to clarify a reason for special handling, must follow RMK/.
ALTRV: for a flight operated in accordance with an altitude reservation
EXAMPLE
STS/ALTRV RMK/ALTRV AT CN718 FL250B270
ATFMX: for a flight approved for exemption from ATFM measures by the appropriate ATS authority;
FFR: firefighting;
FLTCK: flight check for calibration of NAVAIDs;
EXAMPLE
STS/FLTCHK RMK/FLIGHT CHECK ILS RY23 AT YIP
HAZMAT: for a flight carrying hazardous material;
HEAD: a flight with Head of State status;
HOSP: for a medical flight declared by medical authorities;
HUM: for a flight operating on a humanitarian mission;
MARSA: for a flight for which a military entity assumes responsibility for separation of military aircraft;
EXAMPLE
STS/MARSA RMK/IR101 E1802X1817 MARSA BAKER23 AND TOGA17
MEDEVAC: for a life critical medical emergency evacuation;
NONRVSM: for a nonRVSM capable flight intending to operate in RVSM airspace;
SAR: for a flight engaged in a search and rescue mission; and
STATE: for a flight engaged in military, customs or police services.
Other reasons for special handling by ATS must be denoted under the designator RMK/.
PBN/ Indication of RNAV and/or RNP capabilities. Include as many of the applicable descriptors, up to a maximum of 8 entries (not more than 16 characters).
RNAV SPECIFICATIONS
| |
B4 RNAV 5 VOR/DME |
| |
B5 RNAV 5 INS or IRS
|
| A1 RNAV 10 (RNP 10) |
B6 RNAV 5 LORAN C
|
| B1 RNAV 5 all permitted sensors |
C1 RNAV 2 all permitted sensors |
| B2 RNAV 5 GNSS |
C2 RNAV 2 GNSS |
| B3 RNAV 5 DME/DME |
C3 RNAV 2 DME/DME |
| C4 RNAV 2 DME/DME/IRU |
RNP SPECIFICATIONS |
| D1 RNAV 1 all permitted
sensors |
L1 RNP 4 |
| |
O1 Basic RNP 1 all permitted sensors
|
| D2 RNAV 1 GNSS |
O2 Basic RNP 1 GNSS |
| D3 RNAV 1 DME/DME |
O3 Basic RNP 1 DME/DME |
| D4 RNAV 1 DME/DME/IRU |
O4 Basic RNP 1 DME/DME/IRU |
| |
S1 RNP APCH
|
| |
S2 RNP APCH with BAROVNAV
|
| |
T1 RNP AR APCH with RF
(special authorization required)
|
| |
T2 RNP AR APCH without RF
(special authorization required)
|
Combinations of alphanumeric characters not indicated above are reserved.
NAV/ Significant data related to navigation equipment, other than specified in PBN/, as required by the
appropriate ATS authority. Indicate GNSS augmentation under this indicator, with a space between two or more methods
of augmentation, for example, NAV/GBAS SBAS.
NOTE
See paragraph 623 to file NAV/ for flight with Area Navigation (RNAV) Routes in Domestic U.S. airspace.
COM/ Indicate communications applications or capabilities not specified in Item 10(a).
DAT/ Indicate data applications or capabilities not specified in 10(a).
SUR/ Include surveillance applications or capabilities not specified in Item 10(b). If ADSB capability filed in
Item 10 is compliant with RTCA DO260B, include the item “260B” in SUR/. If ADSB capability filed in Item 10 is
compliant with RTCA DO282B, include the item “282B” in SUR/.
EXAMPLE
1. SUR/260B
2. SUR/260B 282B
DEP/ Insert the non−ICAO identifier of departure aerodrome, if ZZZZ is inserted in Item 13, or the ATS unit
from which supplementary flight plan data can be obtained, if AFIL is inserted in Item 13. For aerodromes not listed in
the relevant Aeronautical Information Publication, indicate location as follows:
With 4 figures describing latitude in degrees and tens and units of minutes followed by “N” (North) or “S”
(South), followed by 5 figures describing longitude in degrees and tens and units of minutes, followed by “E” (East) or
“W” (West). Make up the correct number of figures, where necessary, by insertion of zeros, e.g. 4620N07805W
(11 characters).
OR Bearing and distance from the nearest significant point, as follows:
The identification of the significant point followed by the bearing from the point in the form of 3 figures
giving degrees magnetic, followed by the distance from the point in the form of 3 figures expressing nautical miles. In
areas of high latitude where it is determined by the appropriate authority that reference to degrees magnetic is impractical,
degrees true may be used. Make up the correct number of figures, where necessary, by insertion of zeros, e.g., a point
of 180°magnetic at a distance of 40 nautical miles from VOR “DUB” should be expressed as DUB180040.
OR The first point of the route (name or LAT/LONG) or the marker radio beacon, if the aircraft has not
taken off from an aerodrome.
DEST/ Insert the non−ICAO identifier of destination aerodrome, if ZZZZ is inserted in Item 16. For
aerodromes not listed in the relevant Aeronautical Information Publication, indicate location in LAT/LONG or bearing
and distance from the nearest significant point, as described under DEP/ above.
DOF/ The date of flight departure in a six figure format (YYMMDD, where YY equals the year, MM
equals the month and DD equals the day). The FAA will not accept flight plans filed with Date of Flight resulting in more
than 24 hours in advance.
REG/ The nationality or common mark and registration mark of the aircraft, if different from the aircraft
identification in Item 7.
EET/ Significant points or FIR boundary designators and accumulated estimated elapsed times from
takeoff to such points or FIR boundaries, when so prescribed on the basis of regional air navigation agreements, or by
the appropriate ATS authority.
EXAMPLES
EET/CAP0745 XYZ0830
EET/EINN0204
SEL/ SELCAL Code, for aircraft so equipped.
TYP/ Type(s) of aircraft, preceded if necessary without a space by number(s) of aircraft and separated
by one space, if ZZZZ is inserted in Item 9.
EXAMPLE
TYP/2F15 5F5 3B2
CODE/ Aircraft address (expressed in the form of an alphanumerical code of six hexadecimal characters)
when required by the appropriate ATS authority. Example: “F00001” is the lowest aircraft address contained in the
specific block administered by ICAO.
DLE/ En route delay or holding, insert the significant point(s) on the route where a delay is planned to
occur, followed by the length of delay using four figure time in hours and minutes (hhmm).
EXAMPLE
DLE/MDG0030
OPR/ ICAO designator or name of the aircraft operating agency, if different from the aircraft
identification in item 7.
ORGN/ The originator’s 8 letter AFTN address or other appropriate contact details, in cases where the
originator of the flight plan may not be readily identified, as required by the appropriate ATS authority.
NOTE
In some areas, flight plan reception centers may insert the ORGN/ identifier and originator's AFTN address automatically.
PER/ Aircraft performance data, indicated by a single letter as specified in the Procedures for Air
Navigation Services — Aircraft Operations (PANSOPS, Doc 8168), Volume I — Flight Procedures, if so prescribed by
the appropriate ATS authority.
ALTN/ Name of destination alternate aerodrome(s), if ZZZZ is inserted in Item 16. For aerodromes not
listed in the relevant Aeronautical Information Publication, indicate location in LAT/LONG or bearing and distance from
the nearest significant point, as described in DEP/ above.
RALT/ ICAO four letter indicator(s) for enroute alternate(s), as specified in Doc 7910, Location
Indicators, or name(s) of enroute alternate aerodrome(s), if no indicator is allocated. For aerodromes not listed in the
relevant Aeronautical Information Publication, indicate location in LAT/LONG or bearing and distance from the nearest
significant point, as described in DEP/ above.
TALT/ ICAO four letter indicator(s) for takeoff alternate, as specified in Doc 7910, Location Indicators,
or name of takeoff alternate aerodrome, if no indicator is allocated. For aerodromes not listed in the relevant Aeronautical
Information Publication, indicate location in LAT/LONG or bearing and distance from the nearest significant point, as
described in DEP/ above.
RIF/ The route details to the revised destination aerodrome, following by the ICAO fourletter location
indicator of the aerodrome. The revised route is subject to reclearance in flight.
EXAMPLES
RIF/DTA HEC KLAX
RIF/ESP G94 CLA YPPH
RMK/ Any other plain language remarks when required by the appropriate ATS authority or deemed necessary.
ITEM 19: SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Endurance
After E/
ENTER a 4figure group giving the fuel endurance in hours and minutes.
Persons on board
After P/
ENTER the total number of persons (passengers and crew) on board, when required by the
appropriate ATS authority. ENTER TBN (to be notified) if the total number of persons is not known at the time of filing.
Emergency and survival equipment
R/ (RADIO)
CROSS OUT U if UHF on frequency 243.0 MHz is not available.
CROSS OUT V if VHF on
frequency 121.5 MHz is not available. CROSS OUT E if emergency locator transmitter (ELT) is not available.
S/ (SURVIVAL EQUIPMENT)
CROSS OUT all indicators if survival equipment is not carried.
CROSS OUT P if polar survival equipment
is not carried. CROSS OUT D if desert survival equipment is not carried.
CROSS OUT M if maritime survival equipment
is not carried. CROSS OUT J if jungle survival equipment is not carried.
J/ (JACKETS)
CROSS OUT all indicators if life jackets are not carried.
CROSS OUT L if life jackets are not
equipped with lights. CROSS OUT F if life jackets are not equipped with fluorescein.
CROSS OUT U or V or both as
in R/ above to indicate radio capability of jackets, if any.
D/ (DINGHIES)
(NUMBER)
CROSS OUT indicators D and C if no dinghies are carried, or
ENTER number of dinghies carried; and
(CAPACITY)
ENTER total capacity, in persons, of all dinghies carried; and
(COVER) CROSS OUT indicator C if dinghies are not covered; and
(COLOR)
ENTER color of dinghies if carried.
A/ (AIRCRAFT COLOR AND MARKINGS)
ENTER color of aircraft and significant markings.
N/ (REMARKS)
CROSS OUT indicator N if no remarks, or
INDICATE any other survival equipment carried and any other remarks regarding survival equipment.
C/ (PILOT)
ENTER name of pilotincommand.
2.3 Filed by
ENTER the name of the unit, agency or person filing the flight plan.
2.4 Acceptance of the flight plan
Indicate acceptance of the flight plan in the manner prescribed by the appropriate ATS authority.
2.5 Instructions for entering COM data
Items to be completed
COMPLETE the top two shaded lines of the form, and
COMPLETE the third shaded line only when necessary, following
the provisions in PANSATM, Chapter 11, 11.2.1.2, unless ATS prescribes otherwise.
3. Instructions for the Transmission of a
Filed Flight Plan (FPL) Message
3.1
Correction of obvious errors
Unless otherwise prescribed, CORRECT obvious format errors and/or omissions (i.e. oblique
stokes) to ensure adherence as specified in Section 2.
3.2
Items to be transmitted
TRANSMIT items as indicated below, unless otherwise prescribed:
a. the items in the shaded lines, above Item 3;
b.
Starting with <<� (FPL of Item 3:
All symbols and data in the unshaded boxes to the ) <<� at the end of Item 18,
additional alignment functions as necessary to prevent the inclusion of more than 69 characters
in any line of Items 15 and 18. The alignment function is to be inserted only in lieu of a space so as
not to break up a group of data, letter shifts and figure shifts (not preprinted on the form) as necessary;
c.
the AFTN Ending, as described below:
End-of-Text Signal
(1)
one LETTER SHIFT
(2)
two CARRIAGE RETURNS, one LINE FEED
Page-feed Sequence
Seven LINE FEEDS
End-of-Message Signal
Four of the letter N.
4. Instructions for the Transmission of a Supplementary
Flight Plan (SPL) Message
4.1
Items to be transmitted
Transmit items as indicated hereunder, unless otherwise prescribed:
a.
AFTN Priority Indicator, Addressee Indicators <<�, Filing Time, Originator Indicator
<<� and, if necessary, specific identification of addressees and/or originator;
b.
Starting with <<b (SPL: all symbols and data in the unshaded areas of boxes 7, 13, 16, and 18, except
that the `)' at the end of box 18 is not to be transmitted, and then the symbols in the unshaded area of
box 19 down to and including the ) <<b of box 19, additional alignment functions as necessary to prevent
the inclusion of more than 69 characters in any line of Items 18 and 19. The alignment function is to be
inserted only in lieu of a space, so as not to break up a group of data, letter shifts and figure shifts (not
preprinted on the form) as necessary;
(c)
the AFTN Ending, as described below:
EndofText Signal
(1) one LETTER SHIFT
(2) two CARRIAGE RETURNS, one LINE FEED
Pagefeed Sequence
Seven LINE FEEDS
EndofMessage Signal
Four of the letter N.
5. Example of Completed Flight Plan Form

6. ICAO Model Flight Plan, Reverse Side

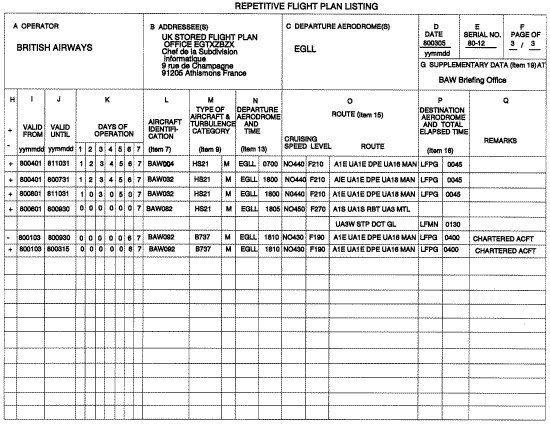
7. ICAO Model Repetitive Flight Plan (RPL) Listing Form

7.1
Instructions for the completion of the repetitive flight plan (RPL) listings form
7.2
General
List only flight plans that will operate in accordance with IFR. (Flight rules I in FPL format).
It is assumed that all aircraft are operating as scheduled flights (Type of flight S in FPL format),
otherwise notify in Q (Remarks).
It is assumed that all aircraft operating on RPL's are equipped with 4096-code transplanters with
modes A and C. Otherwise, notify Q (Remarks).
List flight plans in alphabetical order of the location indicator of the departure aerodrome.
List flight plans for each departure - aerodrome in chronological order of estimated off-block times.
Adhere closely to the data conventions as indicated for the Flight Plan Form
unless otherwise specifically indicated in 7.5.
Insert all clock times in 4 figures UTC.
Insert all estimated elapsed times in 4 figures (hours and minutes).
Insert data on a separate line for each segment of operations with one or more stops; i.e., from
any departure aerodrome to the next destination aerodrome even through call sign or flight number
is the same for multiple segments.
Clearly identify additions and deletions in accordance with Item H at 7.4. Subsequent listings must list
the corrected and added data, and deleted flight plans must be omitted.
Number pages by indicating number of pages and total number of pages in submission.
Utilize more than one line for any RPL where the space provided for items O and Q on one line is not sufficient.
7.3
A flight must be cancelled as follows:
a. indicate a minus sign in item H followed by all other items of the cancelled flight;
b. insert a subsequent entry denoted by a plus sign in item H and the date of the last flight in item J, with all
other items of the cancelled flight unchanged.
7.4
Modification to a flight must be made as follows:
a. carry out the cancellation as indicated in 7.2; and
b. insert a third entry giving the new flight plan(s) with the appropriate items modified as necessary,
including the new validity dates in items I and J.
Note.- All entries related to the same flight will be inserted in succession in the order specified above.
7.5
Instructions for insertion of RPL data
Complete Items A to Q as indicated hereunder.
ITEM A: OPERATOR
INSERT
Name of operator.
ITEM B: ADDRESSEE(S)
INSERT
Name of agency(ies) designated by States to administer RPL's for FIR's or areas of
responsibility concerned with the route of flight.
ITEM C: DEPARTURE AERODROME(S)
INSERT
Location indicator(s) of departure aerodrome(s).
ITEM D: DATE
INSERT
On each page of submission the date (year, month, day) in a 6-figure group that the listing was submitted.
ITEM E: SERIAL NUMBER
INSERT
Serial number of submission (2 numerics) indicating last two digits of year, a dash, and the
sequential number of the submission for the year indicated (start with numeral 1 each new year).
ITEM F: PAGE OF
INSERT
Page number and total number of pages submitted.
ITEM G: SUPPLEMENTARY DATA AT
INSERT
Name of contact where information normally provided under Item 19 of the FPL is kept readily
available and can be supplied without delay.
ITEM H: ENTRY TYPE
INSERT
A minus sign (-) for each flight plan that is to be deleted from the listing.
INSERT
A plus sign (+) for each initial listing and, in the case of subsequent submissions, for each flight plan
not listed in the previous submission.
Note - No information is required under this item for any flight plan which is unchanged from the previous submission.
ITEM I: VALID FROM
INSERT
First date (year, month, day) upon which the flight is scheduled to operate.
ITEM J: VALID UNTIL
INSERT
Last date (year, month, day) upon which the flight is scheduled to operate as listed, or
UFN if the duration is unknown
ITEM K: DAYS OF OPERATION
INSERT
Number corresponding to the day of the week in the appropriate column;
Monday = 1 through Sunday = 7.
INSERT
0 for each day of non-operation in the appropriate column.
ITEM L: AIRCRAFT IDENTIFICATION (Item 7 of the ICAO flight plan)
INSERT
Aircraft identification to be used for the flight.
ITEM M: TYPE OF AIRCRAFT AND WAKE TURBULENCE CATEGORY (Item 9 of the ICAO flight plan)
INSERT
Appropriate ICAO designator as specified in ICAO Doc 8643 - Aircraft Type Designators.
INSERT
H, M or L indicator as appropriate:
H - HEAVY to indicate an aircraft type with a maximum certificated take-off mass of 136,000 kg or more,
M - MEDIUM to indicate an aircraft type with a maximum certificated take-off mass of
less than 136,000 kg but more than 7,000 kg,
L - LIGHT to indicate an aircraft type with a maximum certificated take-off mass of 7,000 kg or less.
ITEM N: DEPARTURE AERODROME AND TIME (Item 13 of the ICAO flight plan)
INSERT
Location indicator of the departure aerodrome.
INSERT
The off-block time, i.e., the estimated time that the aircraft will commence movement associated
with departure.
ITEM O: ROUTE (Item 15 of the ICAO flight plan)
a. Cruising Speed
INSERT
The true airspeed for the first or whole cruising portion of the flight in accordance with Item 15(a)
of the ICAO flight plan.
b. Cruising level
INSERT
The planned cruising level for the first or whole portion of the route in accordance with Item 15(b)
of the ICAO flight plan.
c. Route
INSERT
The entire route in accordance with Item 15(c) of the ICAO flight plan.
ITEM P: DESTINATION AERODROME AND TOTAL ESTIMATED ELAPSED TIME
(Item 16 of the ICAO flight plan)
INSERT
Location indicator of the destination aerodrome.
INSERT
The total estimated elapsed time.
ITEM Q: REMARKS
INSERT
Items of information as required by the appropriate ATS authority, items normally notified in
Item 18 of the ICAO flight plan and any other information pertinent to the flight of concern to ATS.
8. Example of a Completed Repetitive Flight Plan (RPL)
Listing Form
|
