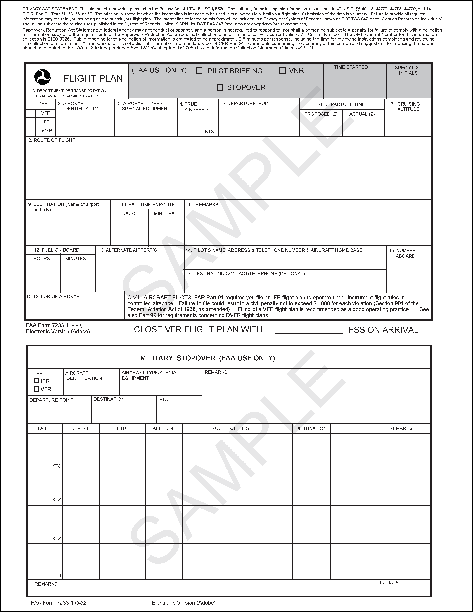
Appendix B. FAA Form 7233-1, Flight Plan
Section 1. General
- Where references are made to FAA Form 7233-1, Flight Plan, and FAA Form 7233-4, International Flight Plan, Department of Defense (DoD) use of the equivalent DoD Forms 175 and 1801 respectively, is implied and acceptable.
- Within U.S. controlled airspace, FAA Form 7233-1, Flight Plan, may be used by filers of DoD/military flight plans and civilian stereo route flight plans.
- Use of the international flight plan format is mandatory for:
- Any flight plan filed, with the exception of DoD flight plans and civilian stereo route flight plans, which can still be filed using the format prescribed in FAA Form 7233-1.
- Any flight that will depart U.S. domestic airspace. For DoD flight plan purposes, offshore warning areas may use FAA Form 7233-1 or military equivalent.
- Any flight requesting routing that requires Performance Based Navigation.
- Any flight requesting services that require filing of capabilities only supported in the international flight plan.
Section 2. Instructions for Flight Plan Items
- Type of flight plan (Item 1). Check the appropriate box:
- VFR for visual flight rules.
- IFR for instrument flight rules.
- DVFR for defense VFR.
- Aircraft identification, call sign. (Item 2).
- Enter two-to-seven alphanumeric characters followed by a space character. The first character of the identification must be a letter. For flight processing systems (for example, ERAM or STARS) which do not accept a call sign that begins with a number:
- If the call sign is six characters or less, add a “Q” at the beginning of the call sign.
- If the call sign is seven characters, delete the first character and replace it with a “Q.” Put the original call sign in the remarks section of the flight plan.
- Civilian aircraft including air carrier.
- For air taxi aircraft, enter the letter/digit registration including the letter “T” prefix.
- For MEDEVAC aircraft, enter the letter “L” at the beginning of the call sign. The letter “L” must not be entered in Item 2 of the flight plan for air carrier or air taxi MEDEVAC aircraft. Include the word “MEDEVAC” in the remarks section of the flight plan.
- For air carriers, enter the three‐letter aircraft company designator specified in FAA Order JO 7340.2, Contractions, followed by the trip or flight number.
- U.S. military aircraft.
- Enter the military abbreviation followed by the last five digits of the aircraft's number. TBL B-1 provides a list of aircraft abbreviations based on military service.
TBL B-1
Military Aircraft AbbreviationsAbbreviation
Military Service
A
U.S. Air Force
C
Coast Guard
E
Air Evacuation
G
Air/Army National Guard
CMB
CAMBER (U.S. Air Force contract)
R
Army
RCH
REACH (U.S. Air Force Air Mobility Command)
S
Special Air Mission (SAM)
VM
Marine Corps
VV
Navy
- For certain tactical mission aircraft, enter the assigned three-to-six letter code word followed by a one-to-four digit number. Aircraft carrying the president, vice president, and/or their family members will use the identifiers in TBL B-2.
TBL B-2
President, Vice President, and Family Call Sign AbbreviationsService
President Code
Family Code
Vice President Code
Family Code
Air Force
AF1
EXEC1F
AF2
EXEC2F
Marine
VM1
EXEC1F
VM2
EXEC2F
Navy
VV1
EXEC1F
VV2
EXEC2F
Army
RR1
EXEC1F
RR2
EXEC2F
Coast Guard
C1
EXEC1F
C2
EXEC2F
Guard
G1
EXEC1F
G2
EXEC2F
Commercial
EXEC1
EXEC1F
EXEC2
EXEC2F
- Enter the military abbreviation followed by the last five digits of the aircraft's number. TBL B-1 provides a list of aircraft abbreviations based on military service.
- Canadian military aircraft. The abbreviations must be followed by a number group not to exceed four digits. TBL B-3 provides a list of Canadian aircraft abbreviations based on military service.
TBL B-3
Canadian Military Aircraft AbbreviationsAbbreviation
Military Service
CFC
Canadian Forces
CTG
Canadian Coast Guard
- Aircraft type (Item 3).
- Enter the standard aircraft type designator, in accordance with FAA Order JO 7360.1, Aircraft Type Designators.
- Prefix to aircraft type (one-to-two alphanumeric characters).
- For IFR operations, if the aircraft's weight class is heavy, indicate this with the prefix “H.”
- If a formation flight is planned, enter the number and type of aircraft (for example, 2H/B52).
- Suffix to aircraft type (one alpha character). Indicate for IFR operations the aircraft's radar transponder, distance measuring equipment (DME), or area navigation (RNAV), including long range navigation (LORAN), capability by adding the appropriate symbol preceded by a slant (/). TBL B-4 shows the aircraft suffix codes based on navigation and transponder capabilities.
TBL B-4
Aircraft Equipment SuffixesNavigation Capability
Transponder Capability
Suffix
RVSM
No GNSS, No RNAV
Transponder with Mode C
/W
RNAV, No GNSS
Transponder with Mode C
/Z
GNSS
Transponder with Mode C
/L
No RVSM
No DME
No transponder
/X
Transponder with no Mode C
/T
Transponder with Mode C
/U
DME
No transponder
/D
Transponder with no Mode C
/B
Transponder with Mode C
/A
TACAN
No transponder
/M
Transponder with no Mode C
/N
Transponder with Mode C
/P
RNAV, No GNSS
No transponder
/Y
Transponder with no Mode C
/C
Transponder with Mode C
/I
GNSS
No transponder
/V
Transponder with no Mode C
/S
Transponder with Mode C
/G
- True airspeed (Item 4).
- Enter two-to-four digits for true airspeed in knots.
- Enter “M” followed by three digits for Mach number.
- Enter “SC” for speed classified.
- Departure point (Item 5). Enter two-to-twelve alphanumeric and slant characters for name or identifier of the departure airport or point over which the flight plan is activated.
- Departure time (Item 6). Enter departure time in coordinated universal time (UTC).
- Cruising altitude (Item 7).
- Enter two-to-seven characters followed by a space character.
- Altitudes or flight levels, as appropriate, must be expressed in hundreds of feet.
- The letters “OTP” must be entered in this field to indicate a requested altitude of VFR conditions‐on‐top.
- Route of flight (Item 8).
- Enter identifiers for airways or jet routes to indicate the proposed flight path.
- For direct flight, use names or identifiers of navigation aids, Navigation Reference System (NRS) waypoints, and geographical points or coordinates.
- If more than one airway or jet route is to be flown, clearly indicate the transition points.
- Destination (Item 9). Enter two-to-twelve alphanumeric and/or slant characters for name or identifier of the destination airport or point over which the flight plan is to be canceled.
- Estimated time en route (Item 10). Enter in hours and minutes the total elapsed time between departure and destination in four‐digit format.
- Remarks (Item 11).
- Enter information necessary for ATC, search and rescue operations, and any other data pertinent to the flight or provided by the pilot.
- For the remarks field only, use 1-80 characters beginning with *, #, $, or %. TBL B-5 provides a description for each special character.
TBL B-5
Remark CodesSpecial Character
Description
*
Transmit remarks to all ARTCCs.
#
Transmit remarks to departure ARTCC only.
$
Transmit remarks only to those addresses in the CP field of the flight notification message.
%
For remarks not to be transmitted.
- Fuel on board (Item 12). Enter in hours and minutes in four‐digit format.
- Alternate airport(s) (Item 13). Enter the location identifier if specified by the pilot.
- Pilot's name, telephone number, and aircraft's home base (Item 14). The pilot's name is not required if BASEOPS or the aircraft operator's name and contact data are provided.
- Number of people on board (Item 15). Enter the number of people on board the aircraft.
- Color of the aircraft (Item 16). Use authorized contractions when available. TBL B-6 provides authorized contractions for aircraft colors.
TBL B-6
Codes for Aircraft ColorsCode
Color
A
Amber
B
Blue
BE
Beige
BK
Black
BR
Brown
G
Green
GD
Gold
GY
Gray
M
Maroon
O
Orange
OD
Olive Drab
P
Purple
PK
Pink
R
Red
S
Silver
T
Tan
TQ
Turquoise
V
Violet
W
White
Y
Yellow
FIG B-1
FAA Form 7233-1, Flight Plan For Military/DoD, Civilian Stereo Route Flight Plan Use Only