ENR 5.1: Prohibited, Restricted, and Other Areas
1. Special Use Airspace
1.1 General
1.1.1 Special use airspace (SUA) consists of that airspace wherein activities must be confined because of their nature, or wherein limitations are imposed upon aircraft operations that are not a part of those activities, or both. SUA areas are depicted on aeronautical charts, except for controlled firing areas (CFA), temporary military operations areas (MOA), and temporary restricted areas.
1.1.2 Prohibited and restricted areas are regulatory special use airspace and are established in 14 CFR Part 73 through the rulemaking process.
1.1.3 Warning areas, MOAs, alert areas, CFAs, and national security areas (NSA) are nonregulatory special use airspace.
1.1.4 Special use airspace descriptions (except CFAs) are contained in FAA Order JO 7400.10, Special Use Airspace.
1.1.5 Permanent SUA (except CFAs) is charted on Sectional Aeronautical, VFR Terminal Area, and applicable En Route charts, and include the hours of operation, altitudes, and the controlling agency.
1.2 Prohibited Areas
1.2.1 Prohibited areas contain airspace of defined dimensions identified by an area on the surface of the earth within which the flight of aircraft is prohibited. Such areas are established for security or other reasons associated with the national welfare. These areas are published in the Federal Register and are depicted on aeronautical charts.
1.3 Restricted Areas
1.3.1 Restricted areas contain airspace identified by an area on the surface of the earth within which the flight of aircraft, while not wholly prohibited, is subject to restrictions. Activities within these areas must be confined because of their nature or limitations imposed upon aircraft operations that are not a part of those activities or both. Restricted areas denote the existence of unusual, often invisible, hazards to aircraft such as artillery firing, aerial gunnery, or guided missiles. Penetration of restricted areas without authorization from the using or controlling agency may be extremely hazardous to the aircraft and its occupants. Restricted areas are published in the Federal Register and constitute 14 CFR Part 73.
1.3.2 ATC facilities apply the following procedures when aircraft are operating on an IFR clearance (including those cleared by ATC to maintain VFR-on-top) via a route which lies within joint-use restricted airspace.
1.3.2.1 If the restricted area is not active and has been released to the controlling agency (FAA), the ATC facility will allow the aircraft to operate in the restricted airspace without issuing specific clearance for it to do so.
1.3.2.2 If the restricted area is active and has not been released to the controlling agency (FAA), the ATC facility will issue a clearance which will ensure the aircraft avoids the restricted airspace unless it is on an approved altitude reservation mission or has obtained its own permission to operate in the airspace and so informs the controlling facility.
1.3.3 Permanent restricted areas are charted on Sectional Aeronautical, VFR Terminal Area, and the appropriate En Route charts.
1.4 Warning Areas
1.4.1 A warning area is airspace of defined dimensions, extending from three nautical miles outward from the coast of the U.S., that contains activity that may be hazardous to nonparticipating aircraft. The purpose of such warning areas is to warn nonparticipating pilots of the potential danger. A warning area may be located over domestic or international waters or both.
2. Other Airspace Areas
2.1 National Security Areas
2.1.1 NSAs consist of airspace of defined vertical and lateral dimensions established at locations where there is a requirement for increased security and safety of ground facilities. Pilots are requested to voluntarily avoid flying through the depicted NSA. When it is necessary to provide a greater level of security and safety, flight in NSAs may be temporarily prohibited by regulation under the provisions of 14 CFR Section 99.7. Regulatory prohibitions will be issued by System Operations Security and disseminated via NOTAM. Inquiries about NSAs should be directed to System Operations Security.
2.2 Temporary Flight Restrictions
2.2.1 General. This paragraph describes the types of conditions under which the FAA may impose temporary flight restrictions. It also explains which FAA elements have been delegated authority to issue a temporary flight restrictions NOTAM and lists the types of responsible agencies/offices from which the FAA will accept requests to establish temporary flight restrictions. The 14 CFR is explicit as to what operations are prohibited, restricted, or allowed in a temporary flight restrictions area. Pilots are responsible to comply with 14 CFR Sections 91.137, 91.138, 91.141, and 91.143 when conducting flight in an area where a temporary flight restrictions area is in effect, and should check appropriate NOTAMs during flight planning.
2.2.2 The purpose for establishing a temporary flight restrictions area is to:
2.2.2.1 Protect persons and property in the air or on the surface from an existing or imminent hazard associated with an incident on the surface when the presence of low-flying aircraft would magnify, alter, spread, or compound that hazard (14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(1)).
2.2.2.2 Provide a safe environment for the operation of disaster relief aircraft (14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(2)).
2.2.2.3 Prevent an unsafe congestion of sightseeing aircraft above an incident or event which may generate a high degree of public interest (14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(3)).
2.2.2.4 Protect declared national disasters for humanitarian reasons in the State of Hawaii (14 CFR Section 91.138).
2.2.2.5 Protect the President, Vice President, or other public figures (14 CFR Section 91.141).
2.2.2.6 Provide a safe environment for space agency operations (14 CFR Section 91.143).
2.2.3 Except for hijacking situations, when the provisions of 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(1) or (a)(2) are necessary, a temporary flight restrictions area will only be established by or through the area manager at the Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) having jurisdiction over the area concerned. A temporary flight restrictions NOTAM involving the conditions of 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(3) will be issued at the direction of the service area office director having oversight of the airspace concerned. When hijacking situations are involved, a temporary flight restrictions area will be implemented through the TSA Aviation Command Center. The appropriate FAA air traffic element, upon receipt of such a request, will establish a temporary flight restrictions area under 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(1).
2.2.4 The FAA accepts recommendations for the establishment of a temporary flight restrictions area under 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(1) from military major command headquarters, regional directors of the Office of Emergency Planning, Civil Defense State Directors, State Governors, or other similar authority. For the situations involving 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(2), the FAA accepts recommendations from military commanders serving as regional, subregional, or Search and Rescue (SAR) coordinators; by military commanders directing or coordinating air operations associated with disaster relief; or by civil authorities directing or coordinating organized relief air operations (includes representatives of the Office of Emergency Planning, U.S. Forest Service, and State aeronautical agencies). Appropriate authorities for a temporary flight restrictions establishment under 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(3) are any of those listed above or by State, county, or city government entities.
2.2.5 The type of restrictions issued will be kept to a minimum by the FAA consistent with achievement of the necessary objective. Situations which warrant the extreme restrictions of 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(1) include, but are not limited to: toxic gas leaks or spills, flammable agents, or fumes which if fanned by rotor or propeller wash could endanger persons or property on the surface, or if entered by an aircraft could endanger persons or property in the air; imminent volcano eruptions which could endanger airborne aircraft and occupants; nuclear accident or incident; and hijackings. Situations which warrant the restrictions associated with 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(2) include: forest fires which are being fought by releasing fire retardants from aircraft; and aircraft relief activities following a disaster (earthquake, tidal wave, flood, etc.). 14 CFR Section 91.137 (a)(3) restrictions are established for events and incidents that would attract an unsafe congestion of sightseeing aircraft.
2.2.6 The amount of airspace needed to protect persons and property or provide a safe environment for rescue/relief aircraft operations is normally limited to within 2,000 feet above the surface and within a 3-nautical-mile radius. Incidents occurring within Class B, Class C, or Class D airspace will normally be handled through existing procedures and should not require the issuance of a temporary flight restrictions NOTAM. Temporary flight restrictions affecting airspace outside of the U.S. and its territories and possessions are issued with verbiage excluding that airspace outside of the 12-mile coastal limits.
2.2.7 The FSS nearest the incident site is normally the “coordination facility.” When FAA communications assistance is required, the designated FSS will function as the primary communications facility for coordination between emergency control authorities and affected aircraft. The ARTCC may act as liaison for the emergency control authorities if adequate communications cannot be established between the designated FSS and the relief organization. For example, the coordination facility may relay authorizations from the on‐scene emergency response official in cases where news media aircraft operations are approved at the altitudes used by relief aircraft.
2.2.8 ATC may authorize operations in a temporary flight restrictions area under its own authority only when flight restrictions are established under 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(2) and (a)(3). The appropriate ARTCC/airport traffic control tower manager will, however, ensure that such authorized flights do not hamper activities or interfere with the event for which restrictions were implemented. However, ATC will not authorize local IFR flights into the temporary flight restrictions area.
2.2.9 To preclude misunderstanding, the implementing NOTAM will contain specific and formatted information. The facility establishing a temporary flight restrictions area will format a NOTAM beginning with the phrase “FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS” followed by: the location of the temporary flight restrictions area; the effective period; the area defined in statute miles; the altitudes affected; the FAA coordination facility and commercial telephone number; the reason for the temporary flight restrictions; the agency directing any relief activities and its commercial telephone number; and other information considered appropriate by the issuing authority.
2. 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(2):
The following NOTAM permits flight operations in accordance with 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(2). The on‐site emergency response official to authorize media aircraft operations below the altitudes used by the relief aircraft.
FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS 25 MILES EAST OF BRANSOME, IDAHO, EFFECTIVE IMMEDIATELY UNTIL 9601202359 UTC. PURSUANT TO 14 CFR SECTION 91.137(A)(2) TEMPORARY FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS ARE IN EFFECT WITHIN A 4-NAUTICAL-MILE RADIUS OF THE INTERSECTION OF COUNTY ROADS 564 AND 315 AT AND BELOW 3,500 FEET MSL TO PROVIDE A SAFE ENVIRONMENT FOR FIRE FIGHTING AIRCRAFT OPERATIONS. DAVIS COUNTY SHERIFF'S DEPARTMENT (792) 555-8122 (122.9) IS IN CHARGE OF ON‐SCENE EMERGENCY RESPONSE ACTIVITIES. GLIVINGS FSS (792) 555-1618 (122.2) IS THE FAA COORDINATION FACILITY.
3. 14 CFR Section 91.137(a)(3):
The following NOTAM prohibits sightseeing aircraft operations.
FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS BROWN, TENNESSEE, DUE TO OLYMPIC ACTIVITY. EFFECTIVE 9606181100 UTC UNTIL 9607190200 UTC. PURSUANT TO 14 CFR SECTION 91.137(A)(3) TEMPORARY FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS ARE IN EFFECT WITHIN A 3-NAUTICAL-MILE RADIUS OF N355783/W835242 AND VOLUNTEER VORTAC 019 DEGREE RADIAL 3.7 DME FIX AT AND BELOW 2,500 FEET MSL. NORTON FSS (423) 555-6742 (126.6) IS THE FAA COORDINATION FACILITY.
4. 14 CFR Section 91.138:
The following NOTAM prohibits all aircraft except those operating under the authorization of the official in charge of associated emergency or disaster relief response activities, aircraft carrying law enforcement officials, aircraft carrying personnel involved in an emergency or legitimate scientific purposes, carrying properly accredited news media, and aircraft operating in accordance with an ATC clearance or instruction.
FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS KAPALUA, HAWAII, EFFECTIVE 9605101200 UTC UNTIL 9605151500 UTC. PURSUANT TO 14 CFR SECTION 91.138 TEMPORARY FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS ARE IN EFFECT WITHIN A 3-NAUTICAL-MILE RADIUS OF N205778/W1564038 AND MAUI /OGG/ VORTAC 275 DEGREE RADIAL AT 14.1 NAUTICAL MILES. JOHN DOE 808-757-4469 OR 122.4 IS IN CHARGE OF THE OPERATION. HONOLULU /HNL/ 808- 757-4470 (123.6) FSS IS THE FAA COORDINATION FACILITY.
5. 14 CFR Section 91.141:
The following NOTAM prohibits all aircraft.
FLIGHT RESTRICTIONS STILLWATER, OKLAHOMA, JUNE 21, 1996. PURSUANT TO 14 CFR SECTION 91.141 AIRCRAFT FLIGHT OPERATIONS ARE PROHIBITED WITHIN A 3-NAUTICAL-MILE RADIUS, BELOW 2000 FEET AGL OF N360962/ W970515 AND THE STILLWATER /SWO/ VOR/DME 176 DEGREE RADIAL 3.8-NAUTICAL-MILE FIX FROM 1400 LOCAL TIME TO 1700 LOCAL TIME JUNE 21, 1996 UNLESS OTHERWISE AUTHORIZED BY ATC.
6. 14 CFR Section 91.143:
The following NOTAM prohibits any aircraft of U.S. registry, or pilot of any aircraft under the authority of an airman certificate issued by the FAA.
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER SPACE OPERATIONS AREA EFFECTIVE IMMEDIATELY UNTIL 9610152100 UTC. PURSUANT TO SECTION 91.143, FLIGHT OPERATIONS CONDUCTED BY FAA CERTIFICATED PILOTS OR CONDUCTED IN AIRCRAFT OF U.S. REGISTRY ARE PROHIBITED AT ANY ALTITUDE FROM SURFACE TO UNLIMITED, WITHIN THE FOLLOWING AREA 30-NAUTICAL-MILE RADIUS OF THE MELBOURNE /MLB/ VORTAC 010 DEGREE RADIAL 21-NAUTICAL-MILE FIX. ST. PETERSBURG, FLORIDA, /PIE/ FSS 813-545-1645 (122.2) IS THE FAA COORDINATION FACILITY AND SHOULD BE CONTACTED FOR THE CURRENT STATUS OF ANY AIRSPACE ASSOCIATED WITH THE SPACE SHUTTLE OPERATIONS. THIS AIRSPACE ENCOMPASSES R2933, R2932, R2931, R2934, R2935, W497A AND W158A. ADDITIONAL WARNING AND RESTRICTED AREAS WILL BE ACTIVE IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE OPERATIONS. PILOTS MUST CONSULT ALL NOTAMS REGARDING THIS OPERATION.
2.3 Parachute Jump Aircraft Operations
2.3.1 Procedures relating to parachute jump areas are contained in 14 CFR Part 105. Tabulations of parachute jump areas in the U.S. are contained in the Chart Supplement.
2.3.2 Pilots of aircraft engaged in parachute jump operations are reminded that all reported altitudes must be with reference to mean sea level, or flight level, as appropriate, to enable ATC to provide meaningful traffic information.
2.3.3 Parachute Operations in the Vicinity of an Airport Without an Operating Control Tower. There is no substitute for alertness while in the vicinity of an airport. It is essential that pilots conducting parachute operations be alert, look for other traffic, and exchange traffic information as recommended in GEN 3.3, paragraph 9.2, Traffic Advisory Practices at Airports Without Operating Control Towers. In addition, pilots should avoid releasing parachutes while in an airport traffic pattern when there are other aircraft in that pattern. Pilots should make appropriate broadcasts on the designated Common Traffic Advisory Frequency (CTAF), and monitor that CTAF until all parachute activity has terminated or the aircraft has left the area. Prior to commencing a jump operation, the pilot should broadcast the aircraft's altitude and position in relation to the airport, the approximate relative time when the jump will commence and terminate, and listen to the position reports of other aircraft in the area.
2.4 Special Air Traffic Rules (SATR) and Special Flight Rules Area (SFRA)
2.4.1 Background. The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) prescribes special air traffic rules for aircraft operating within the boundaries of certain designated airspace. These areas are listed in 14 CFR Part 93 and can be found throughout the NAS. Procedures, nature of operations, configuration, size, and density of traffic vary among the identified areas.
2.4.2 SFRAs. Airspace of defined dimensions, above land areas or territorial waters, within which the flight of aircraft is subject to the rules set forth in 14 CFR Part 93, unless otherwise authorized by air traffic control. Not all areas listed in 14 CFR Part 93 are designated SFRA, but special air traffic rules apply to all areas described in 14 CFR Part 93.
2.4.3 Participation. Each person operating an aircraft to, from, or within airspace designated as a SATR area or SFRA must adhere to the special air traffic rules set forth in 14 CFR Part 93, as applicable, unless otherwise authorized or required by ATC.
2.4.4 Charts. SFRAs are depicted on VFR sectional, terminal area, and helicopter route charts. (See FIG ENR 5.1-1.)
SFRA Boundary
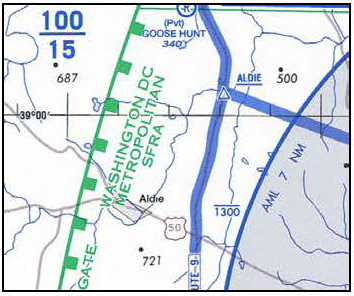
2.4.5 Washington DC Special Flight Rules Area (SFRA) including the Flight Restricted Zone (FRZ). A pilot conducting any type of flight operation in the Washington DC SFRA/FRZ must comply with the requirements in:
2.4.5.1 14 CFR Section 93.339 Washington, DC Metropolitan Area Special Flight Rules Area including the FRZ.
2.4.5.2 14 CFR Section 91.161 Special Awareness Training for the DC SFRA/FRZ, also located on the FAA website at https://www.faasafety.gov/.
2.4.5.3 Any 14 CFR Section 99.7 special security instructions for the DC SFRA/FRZ published via NOTAM by FAA in the interest of national security.
2.5 Weather Reconnaissance Area (WRA)
2.5.1 General. Hurricane Hunters from the United States Air Force Reserve 53rd Weather Reconnaissance Squadron (WRS) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Aircraft Operations Center (AOC) operate weather reconnaissance/research aircraft missions, in support of the National Hurricane Operations Plan (NHOP), to gather meteorological data on hurricanes and tropical cyclones. 53rd WRS and NOAA AOC aircraft normally conduct these missions in airspace identified in a published WRA Notice to Airmen (NOTAM).
2.5.2 WRAs. Airspace with defined dimensions and published by a NOTAM, which is established to support weather reconnaissance/research flights. ATC services are not provided within WRAs. Only participating weather reconnaissance/research aircraft from the 53rd WRS and NOAA AOC are permitted to operate within a WRA. A WRA may only be established in airspace within U. S. Flight Information Regions (FIR) outside of U. S. territorial airspace.
2.5.3 A published WRA NOTAM describes the airspace dimensions of the WRA and the expected activities within the WRA. WRAs may border adjacent foreign FIRs, but are wholly contained within U.S. FIRs. As ATC services are not provided within a WRA, non-participating aircraft should avoid WRAs, and IFR aircraft should expect to be rerouted to avoid WRAs.