Manassas Regional Airport/Harry P. Davis Field (HEF)
Manassas Regional Airport/Harry P. Davis Field (HEF) is a public airport that serves the Washington, DC region. It is located five miles southwest of the city of Manassas and 28 miles from Washington, DC. HEF is the largest general aviation airport in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Traffic is primarily comprised of transient and local GA aircraft. HEF also serves law enforcement, military, and medivac aircraft and numerous flight schools. View a printable Pilot Handbook of the HEF information found on this Web page.
Know Before You Go
HEF Tower Hours of Operation 0630L-2230L
Administrative Office Open 0730L to 1600L M-F
Business Phone 703-361-5800
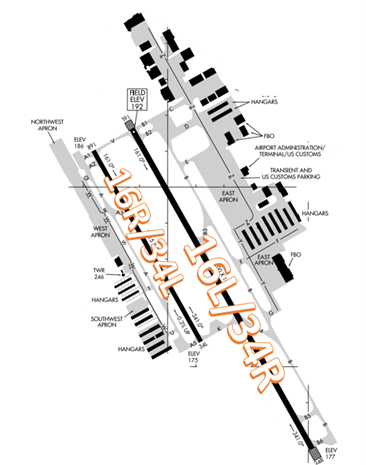
The airport configuration consists of parallel RWYs designated 16L/34R and 16R/34L. General Aviation services are located on the eastside of the airfield.
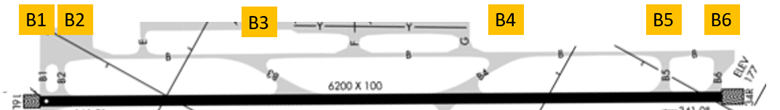
Taxiway Renaming: Connecting TWYs Bravo 1 through Bravo 6 have recently been renamed. Always consult the latest airport diagram and NOTAMs.
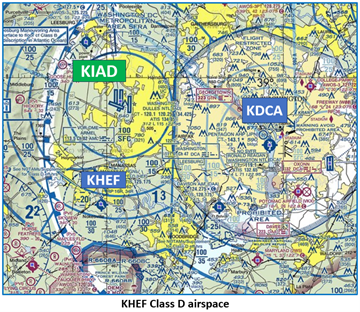
The airspace at HEF is Class D. (Refer to Sectional Chart)
Below find various HEF-specific information and things to be aware of, as well as general information to inform your preflight planning. This will be reviewed quarterly and updated as needed. This information is to supplement the From the Flight Deck Videos that are produced by the FAA Runway Safety Group. Here you will also find information provided by the local air traffic controllers at the airport where you intend to fly. The information is subject to change. Not for navigation or legal* pre-flight action. Always refer to official pre-flight materials such as, but not limited to, NOTAMs, airport diagrams, VFR charts and airport construction notices for the latest airport-specific details.
The Washington D.C. Metropolitan Area Special Flight Rules Area (DC SFRA) is roughly a circular area with a 30 nautical mile (about 33 statute miles) radius around Washington, D.C., and surrounds the Flight-Restricted Zone (FRZ). HEFs Class D is within the SFRA. If flying in and out of HEF, pilots must complete the SFRA online course.
All VFR flights departing or entering the Class D, must file an SFRA flight plan with an entry/exit gate. All aircraft will be given basic SFRA flight following. Any further requests should be made with Potomac TRACON. HEF can only advise Potomac of the pilot's request.
VFR aircraft doing pattern work wishing to remain in the Class D airspace do not need to file a SFRA VFR flight plan.
Potomac Approach Control (PCT) has established internal procedures to track all aircraft within the SFRA for security purposes in conjunction with the published NOTAMs and in accordance with 14 CFR 93.339 (C) regarding the Washington, DC Special Flight Rules Area (SFRA). Pilots should review NOTAMs for the Letter to Airmen: LTA-PCT-43 “SFRA PATTERN WORK OPERATIONS” for specific details.
Hot Spots
- There are no Hotspots.
Wrong Surface Landing Risk - See Arrival Alert Notice for HEF
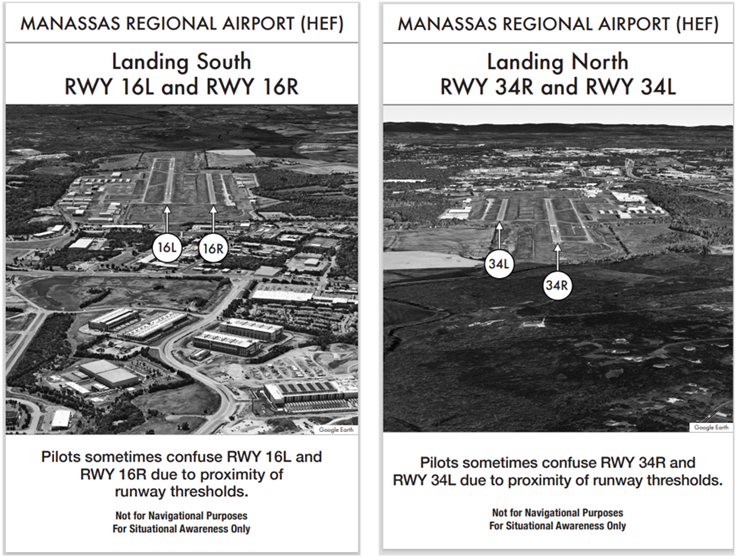
- Wrong Surface landing risk exists with parallel RWYs, especially those with full-length parallel TWYs.
- When RWYs are staggered, remember that the first RWY that becomes visible may not be your assigned RWY.
- RWY 16L is longer and wider than RWY 16R and has an over-run at the approach end. Though both RWY’s have GPS approaches, RWY 16L has a precision approach including a Localizer/Glideslope and Approach Lights.
- RWY 34R has an over-run, is longer and wider, and comes into sight before the shorter RWY 34L. RWY 34R also has approach lights with flashers.
- Runway Markings are White. Surfaces not used for Takeoff/Landing like Taxiway Markings, Chevrons, Runway Shoulder, and Runway Turn-on Markings, etc., are Yellow.
- Loading an instrument approach or GPS Waypoint and verifying heading versus the RWY cleared will help pilots ensure that they are lined up for the correct RWY.
Additional Cautions
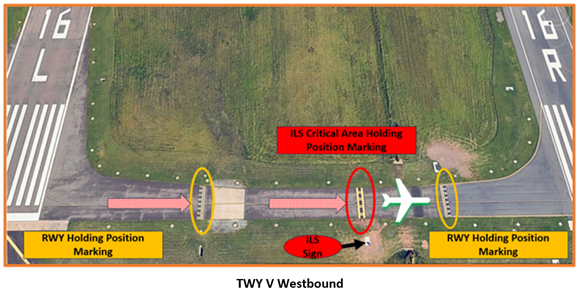
- When taxiing eastbound on TWY V, hold short of the ILS Critical line when the ILS is in use and the weather is less than 800 feet and 2 miles. Aircraft taxiing beyond this point may interfere with the ILS signal to approaching aircraft.
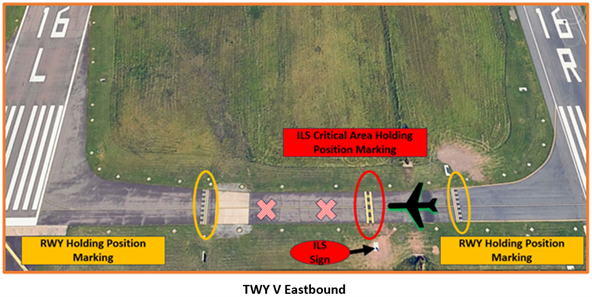
- Conversely, when taxiing across RWY 16L westbound on TWY V, taxi beyond the ILS Critical line when the ILS is in use and the weather is less than 800 feet and 2 miles.
General
- HEF is located 28 miles WSW of Washington D.C. and is within the SFRA.
- Most traffic departs west to exit the SFRA or is inbound from the west. Be vigilant for traffic.
- Runway changes are common.
- Line Up and Wait (LUAW) and Land and Hold Short (LAHSO) operations are not authorized.
- Most GA services are provided by facilities on the east side of the airfield.
Traffic Patterns
- HEF will accommodate pattern work as much as possible, but due to volume may restrict aircraft to a full stop taxi back.
- Pattern Altitudes:
- Helicopter 1000’ MSL
- Single engine and small piston-powered twin 1200’ MSL
- Jets, medium twin engine, and turboprop 1500’ MSL
- Aircraft with malfunctioning ADS-B Out cannot conduct pattern work without prior coordination and approval.
- Be prepared to land on a different RWY than you departed.
- Pilots may be asked to extend upwind, downwind, or make a 360-degree turn. This is to accommodate traffic demand.
Weather
- Mornings can be foggy on the airport grounds, but clear in the sky.
- As the sun sets, departing traffic may not be able to see opposite direction inbound traffic from the west. Inbound traffic will have a better chance to see and avoid as they do not have the sun in their eyes.
Ground Control
- The ramp is uncontrolled, however do not block an entrance to the ramp without contacting Ground Control (GC).
- Advise GC of your location when requesting taxi instructions. Be specific.
- Review Manassas Regional Airport Special Taxi Instructions under Pilot Information for tips and suggestions.
Taxiway Renaming
- Connecting TWYs Bravo 1 through Bravo 6 have recently been renamed.
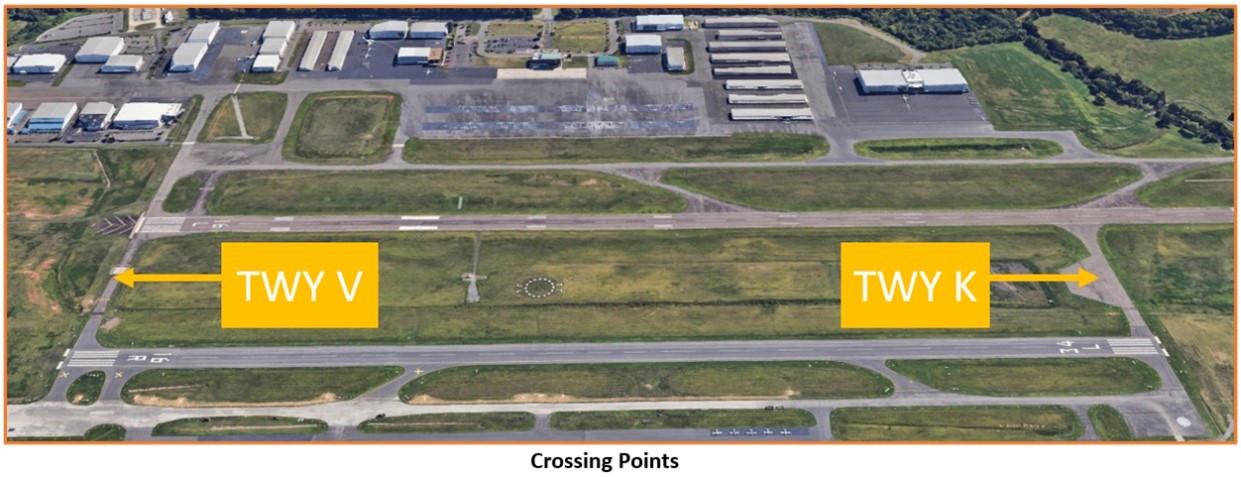
Runway Crossings
- TWY K and TWY V connect the parallel runways. They are the only crossing points if wanting to relocate to/from the east or west side of the airport.
- Read back all hold short instructions with your call sign.
- Hold short at the correct markings. If unsure, ask the TWR.
Takeoff/Departure
- When departing on an IFR flight plan, climb via the SID except maintain 2000’ as issued by Clearance Delivery.
- When departing VFR, do not squawk 1200. Squawk ATC assigned code.
- Small, single-engine aircraft be prepared to depart runway 34L/16R to avoid a delay.
- HEF allows for intersection departures. Request the distance remaining from TWR.
- A delay for wake turbulence for intersection departures may be required.
Arrival/Landing
- Potomac Approach will sequence all IFR aircraft. HEF ATCT may change the RWY assignment and/or sequence due to VFR traffic volume.
- Potomac Approach Control (PCT) will provide IFR separation to VFR aircraft conducting practice instrument approaches. Review NOTAMS for the Letter to Airmen: LTA-PCT-42 “VFR Practice Instrument Approaches” for more information.
Noise Abatement
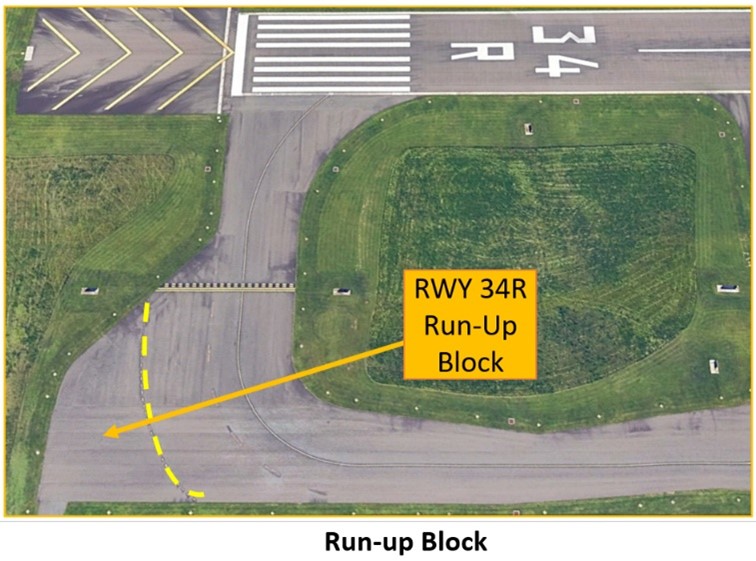
- IFR noise abatement procedures are voluntary. However, be aware that the RWY 34R Run-up Block is the only area where late night or early morning noise is a nuisance.
Additional Information
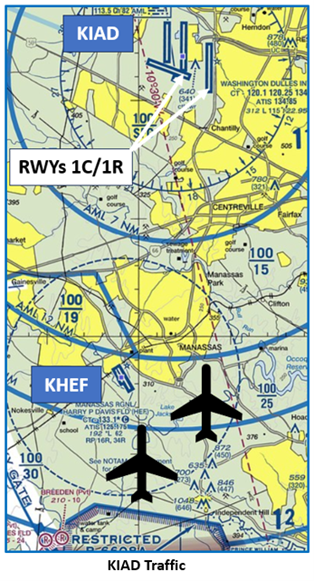
- When Dulles (IAD) is in a north configuration landing RWYs 1C/1R, be cautious of turbo jets over the top of HEF at 2000’. HEF is not in radio communication with these aircraft.