McDonnell Douglas MD-82

Photo copyright Hector A Rivera-SJU - used with permission
American Airlines Flight 1420, N215AA
Little Rock, Arkansas
June 1, 1999
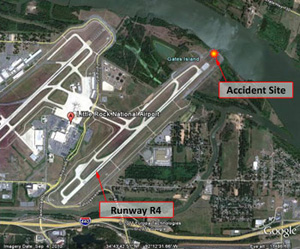
Shortly before midnight on the evening of June 1, 1999, American Airlines Flight 1420 crashed after the aircraft overran the end of runway 4R during landing at Little Rock National Airport in Little Rock, Arkansas. After departing the end of the runway, the airplane struck supporting structure for the instrument landing system localizer array, located 411 feet beyond the end of the runway. The aircraft continued through a chain link fence and over a rock embankment into a flood plain, where it came to rest after colliding with the runway 22L approach lighting support structure. The captain and ten passengers were killed. The first officer, flight attendants and 105 passengers received serious or minor injuries, and 24 passengers were not injured. The airplane was destroyed by impact forces and a post-crash fire.
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) determined that the probable causes of this accident were "the flight crew's failure to discontinue the approach when severe thunderstorms and their associated hazards to flight operations had moved into the airport area, and the crew's failure to ensure that the spoilers had extended after touchdown. Contributing to the accident were the flight crew's (1) impaired performance resulting from fatigue and the situational stress associated with the intent to land under the circumstances, (2) continuation of the approach to a landing when the company's maximum crosswind component was exceeded, and (3) use of reverse thrust greater than 1.3 engine pressure ratio after landing."

Photo copyright Matthew Smith - used with permission
History of the Flight
On June 1, 1999, American Airlines Flight 1420 was a regularly scheduled flight from the Dallas-Fort Worth International Airport, in Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas, to the Little Rock National Airport in Little Rock, Arkansas. This flight was the third and final leg of the first day of a three-day sequence for the flight crew. The flight crew checked in for duty at O'Hare International Airport, Chicago, Illinois about 1030 Central Daylight Time (CDT). The flight sequence began at 1143 with a flight from Chicago to Salt Lake City, Utah. The second leg was a flight from Salt Lake City for Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas. Flight 1420 was scheduled to depart at 2028 CDT and arrive at 2141. However, the airplane originally intended for the flight was delayed in its arrival to Dallas/Fort Worth because of the adverse weather. The delay became a concern to the flight crew since they did not want to exceed the American Airlines crew duty time limitation. To minimize the delay, American Airlines substituted the accident airplane for Flight 1420, and the flight finally departed at about 2240, two hours and 12 minutes later than scheduled. The captain was the flying pilot and the first officer was the non-flying pilot.
Prior to Flight 1420's departure and during the flight, the flight crew received weather advisories for an area of severe thunderstorms along the planned route. The flight crew did not discuss the option of delaying or diverting the landing at Little Rock because of the weather. While en route, the flight crew received a National Weather Service Convective SIGMET (significant meteorological information) weather advisory for an area of severe thunderstorms that included the Little Rock airport area. The cockpit voice recorder (CVR) indicated that the flight crew had discussed the weather and the need to expedite the approach.
Upon the flight's arrival in the Little Rock area, the Little Rock Air Traffic Control Tower (ATCT) controller advised the flight crew that a thunderstorm located northwest of the airport was moving through the area and that the wind was 280 degrees at 28 knots gusting to 44 knots. The first officer told the controller that he and the captain could see the lightning. The controller told the flight crew to expect an instrument landing system (ILS) approach to runway 22L. The first officer believed that, during the descent into the terminal area, the weather was about 15 miles away from the airport and that he and the captain thought there was "some time" to make the approach.
The CVR indicated that the captain and first officer discussed American Airlines' crosswind limitation for landing. The captain indicated that 30 knots was the crosswind limitation but realized that he had provided the limitation for a dry runway. The captain then stated that the wet runway crosswind limitation was 20 knots, but the first officer stated that the limitation was 25 knots. The accident report stated that neither the first officer nor the captain checked the actual crosswind limitation in American's flight manual. The first officer had taken the manual out but the captain signaled him to put the manual away because the captain was confident that the crosswind limitation was 20 knots.

Photo copyright Chris Sharps - used with permission
View Larger
About 11 minutes prior to landing, the controller notified Flight 1420 of a windshear alert, reporting that the centerfield wind was 340 degrees at 10 knots, the north boundary wind was 330 degrees at 25 knots, and the northwest boundary wind was 010 degrees at 15 knots. The flight crew requested runway 4R so that there would be a headwind, rather than a tailwind, during landing. The controller provided Flight 1420 with vectors to the runway 4R ILS final approach course. The vectors turned the airplane away from the airport and clear of the thunderstorm that had previously been reported by the controller. During that time, the first officer conducted an abbreviated approach briefing by stating the localizer frequency and course, the decision altitude, the minimum safe altitude, and a portion of the missed approach procedure for runway 4R.
About eight minutes prior to landing, the controller told the flight crew that the second part of the thunderstorm was apparently moving through the area and that the winds were 340 degrees at 16 knots gusting to 34 knots. The flight crew discussed the option to accept "a short approach" and "keep it in tight." The captain was having difficulty seeing the airport, but relied on the first officer's visual contact with the airport. After the first officer told the controller that the airport was in sight, the controller offered a visual approach for runway 4R, and the first officer accepted. The controller cleared Flight 1420 to land and indicated that the winds were 330 degrees at 21 knots. Shortly thereafter, the flight crew informed the controller that they had lost sight of the airport because of a cloud between the airplane and the airport. The controller then provided radar vectors for the ILS approach to runway 4R. The vectors positioned the airplane on final approach near the ILS outer marker, which is about six miles from the runway.
-NTSB Report
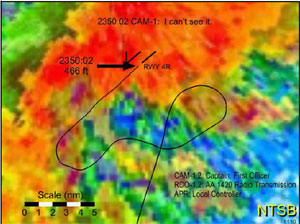
About three minutes prior to landing, the controller reported that there was heavy rain at the airport, the visibility was less than one mile, and the runway visual range (RVR) for runway 4R was 3,000 feet. The first officer acknowledged this information. The controller again cleared Flight 1420 to land and indicated that the wind was 350 degrees at 30 knots, gusting to 45 knots. The first officer then read back the wind information as 030 degrees at 45 knots. About two minutes prior to landing, the controller issued a second windshear alert for the airport, reporting that the centerfield wind was 350 degrees at 32 knots, gusting to 45 knots; the north boundary wind was 310 degrees at 29 knots; and the northeast boundary wind was 320 degrees at 32 knots. This transmission was not acknowledged by the flight crew. The captain asked the first officer to add 20 knots to the landing reference airspeed.
The controller reported that the runway 4R RVR was now 1,600 feet. The captain indicated to the first officer that the flight was established on final approach. The first officer informed the controller that the flight was established on the inbound portion of the ILS. The controller repeated the clearance to land; stated that the wind was 340 degrees at 31 knots, the north boundary wind was 300 degrees at 26 knots, and the northeast boundary wind was 320 degrees at 25 knots; and repeated the RVR. The first officer acknowledged this information. The controller did not receive any further transmissions from Flight 1420.

-NTSB
About one minute prior to landing, the first officer asked the captain if he wanted the flaps set to the 40-degree setting. The captain indicated that he thought he had already called for the landing flaps, after which the first officer set the flaps to 40 degrees. Then the controller informed the flight crew that the wind was 330 degrees at 28 knots. Shortly thereafter, CVR data indicated that the captain said, "this is a can of worms."
At about 2350, after the ground proximity warning system (GPWS) radio altitude callout "sink rate," the airplane touched down on the runway. Over a seven-second period after touchdown, both thrust reversers were deployed and the left and right engines' engine pressure ratios (EPR) reached settings of 1.89 and 1.67, respectively. The thrust reversers were subsequently moved to the unlocked status (neither deployed nor stowed). The flight spoilers did not deploy at touchdown.

-NTSB
Flight 1420 crashed when it overran the end of runway 4R. After departing the end of the runway, the airplane struck several tubes extending outward from the left edge of the instrument landing system (ILS) localizer array, located 411 feet beyond the end of the runway; passed through a chain link security fence; went down a rock embankment to a flood plain located approximately 15 feet below the runway elevation; and collided with the structure supporting the runway 22L approach lighting system. The airplane came to rest about 800 feet from the departure end of runway 4R. The captain and ten passengers were killed; the first officer, the flight attendants, and 105 passengers received serious or minor injuries; and 24 passengers were not injured. The airplane was destroyed by impact forces and a post-crash fire.
The NTSB created an animation showing the accident sequence. The animation can be viewed below: Note: This animation does not have sound. (NTSB Animation - American Flight 1420)
Braking System
The MD-82 main landing gear wheels are equipped with hydraulically powered multi-disc brakes and anti-skid control. The nose wheels are not equipped with brakes. The accident aircraft was equipped with the optional automatic braking (autobrake) system. The brakes may be operated manually by either pilot or applied automatically by the autobrake system. The captain of Flight 1420 elected to use only manual braking during the landing at Little Rock.

-NTSB
The antiskid braking system adapts braking pressure (applied manually or automatically) to runway conditions by sensing an impending skid condition and adjusting brake pressure on each individual wheel to allow for maximum braking performance. The inboard brakes have touchdown protection to prevent them from being applied before or at touchdown. The outboard brakes do not have touchdown protection.
The autobrake system, when armed, automatically applies airplane brakes after touchdown or during a rejected takeoff. The autobrakes will operate only if the spoiler handle is in the extended position. Brake application by the autobrake system begins between one and three seconds after landing. The autobrake system may be unarmed so that the braking function is returned to the pilots. The system is unarmed manually by any of the following actions: pressing any brake pedal more than 25% of its maximum travel, advancing any throttle out of the near-idle range, moving the arm switch to the DISARM position, or returning the spoiler handle to the stowed position.
The NTSB noted that on the accident landing, initial application of manual braking occurred five seconds after touchdown, and full application of the manual brakes did not occur until about 11 seconds after touchdown. The NTSB report also included a summary of the American Airlines DC-9 operating manual section that described the use of aggressive manual braking on short or slippery runways. The Operating Manual stated that on short or slippery runways, full braking (applied by full-brake pedal travel) should be used immediately after nose gear touchdown.
-NTSB Report
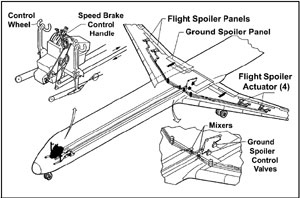
Speed Brake/Ground Spoiler System
The MD-82 airplane has one ground spoiler, one inboard flight spoiler, and one outboard flight spoiler on each wing. Each of the flight spoilers is extended and retracted by its own hydraulic actuator. The flight spoilers are manually operated through the aileron control system by either the control wheel or the spoiler handle in the cockpit. A control wheel input can supplement lateral control (provided by the ailerons) by extending the flight spoilers on the downward-moving wing to a maximum of 60º. An input from the spoiler handle extends the flight spoilers symmetrically on both wings to a maximum of 35º in flight (referred to as the speed brake function) and a maximum of 60º on the ground. A spring-loaded torsion bar mechanically holds the flight spoilers in the retract position when they are not extended.

and thrust reversers
Photo copyright John Farrington - used with permission
The ground spoilers are manually operated by an input from the spoiler handle on the cockpit center pedestal and electrical signals from the proximity system electronic unit via several spoiler control relays. The ground spoilers are extended to 60º only during landing or a rejected takeoff. The ground spoilers are locked down by hydraulic power and a mechanical over-center link during all other phases of flight.
The ground and flight spoilers can be automatically operated by the autospoiler system. To use the autospoiler system for landing, a pilot raises the spoiler handle up to the ARM position (before touchdown), which reveals a red ARM indicator stripe, and positions the roller on the spoiler handle in front of an autospoiler crank arm. The red indicator stripe provides a visual cue to the flight crew that the autospoiler system is armed. After touchdown, the autospoiler switching unit commands the autospoiler actuator to move the crank arm, which in turn moves the spoiler handle fully aft when either the wheel spin-up transducers signal main wheel spin-up or the ground control nose oleo switches signal nose gear touchdown (in case of a failure of the spin-up transducers).

-NTSB Report
Thrust Reversers
The reversers are hydraulically powered, target type, and are intended for ground use only. The thrust reverser on each engine consists of two deflector doors which, when stowed, form the aft nacelle fairing. When extended, the doors redirect engine exhaust gases forward, over and under the nacelle to provide reverse thrust. To prevent accidental extension, separate hydraulically actuated latches prevent the reversers from moving out of the stowed position until the thrust reverser lever (one for each engine) in the flight deck is moved toward the reverse thrust position.

Photo copyright Muchswatch - used with permission
Following reverser extension, movement of the reverser levers controls the amount of reverse thrust available. Up and aft movement of the levers increases reverse thrust, while forward and down movement of the levers deceases reverse thrust. With the levers at idle reverse thrust (a detent is felt on the levers) the engines are allowed to decelerate to idle prior to selection of forward thrust. Movement of the levers full forward and down selects forward idle and deactivates reverse thrust. When the reversers stow, all indicator lights are extinguished.
At the safety board's public hearing on this accident, information was presented regarding MD-80 rudder effectiveness during reverse thrust operation. During reverse thrust operation, the overall effectiveness of the rudder to steer the airplane could be reduced because of the disrupted air flow over the rudder and the vertical stabilizer. The thrust reversers disrupt the air that would normally be flowing in a streamline across the rudder and vertical stabilizer, creating a field of turbulent air.
An MD-80 traveling at 90 to 100 knots with a 1.6 EPR (dry runway) setting would lose directional control from the rudder. Because of the reduced rudder effectiveness, it was recommended by the manufacturer that reverse thrust be discontinued until the airplane was going in the intended direction and that, once directional control from the rudder is restored, reverse thrust could be reapplied.
On February 15, 1996, McDonnell Douglas issued an all-operators letter to all MD-80 operators regarding handling characteristics when landing on wet or slippery runways and a change to reverse thrust management techniques. The letter stated that, because of the reverser efflux pattern resulting from the MD-80's canted reverse thrust buckets, "the aerodynamic forces acting on the vertical stabilizer and rudder are disrupted by an increase in reverse thrust above approximately 1.3 EPR, thus reducing the ability of the rudder and vertical stabilizer to provide optimum directional control." The letter further stated that, "as reverse thrust increases above approximately 1.3 EPR, rudder and vertical stabilizer effectiveness continue to decrease until, at reverse thrust greater than approximately 1.6 EPR, the rudder and vertical stabilizer provide little or no directional control. "Flight 1420 FDR data indicated that during the landing roll, when thrust reverse was above idle, values always exceeded the manufacturer recommended level of 1.3 EPR.
Airplane Stopping Performance
As part of an airplane's certification, a manufacturer must demonstrate the distance to land from a 50-foot height to a complete stop (14 CFR 25.125). The MD-80 "demonstrated landing distance" was measured in two parts - the air distance, from 50 feet to touchdown, and the ground distance, from touchdown to stop - and on a dry, hard-surfaced runway. The operating requirements in 14 CFR Part 121 (Part 121) provide for additional safety margins beyond the demonstrated landing distance, specifically, variations in the speed, touchdown point, runway surface condition, tire condition, temperature, and runway slope. The Part 121 minimum dry runway length is the demonstrated landing distance plus 67 percent. The Part 121 minimum wet runway length is the minimum dry runway length plus 15 percent. The manufacturer presented information to the NTSB regarding the required landing distances for an MD-80 with a landing weight of 127,000 pounds. The actual demonstrated landing distance was 2,830 feet, so the Part 121 minimum dry and wet runway lengths were 4,715 and 5,425 feet, respectively. The estimated landing weight of Flight 1420 was 127,749 pounds. Runway 4R/22L at Little Rock National Airport is 7,200 feet in length, so there was about an 1,800-foot margin between the required minimum wet runway length and the end of the runway.

Photo copyright Tim Perkins - used with permission
The NTSB evaluated the effects of various deceleration devices on Flight 1420's stopping distance with the Boeing Company's MD-80 Operational Landing Program. Computer runs were made to test airplane deceleration with different combinations of spoiler deployment, reverse thrust, and braking scenarios. Selected computer runs showing ground speed versus distance from the runway 4R threshold were compared with Flight 1420's calculated ground speed profile. All of the selected computer runs were based on an initial ground speed of 162 knots, which was close to the 160-knot touchdown ground speed determined from the ground trajectory calculation, and an initial position on the runway of 2,000 feet from the threshold, which was about the point where Flight 1420's tire markings began. Constant, symmetrical reverse thrust at 1.3 EPR was maintained until the ground speed was zero, and all of the braking was based on Flight 1420's braking profile.
Two computer runs demonstrated that proper spoiler deployment is critical to deceleration and stopping distance. Without reverse thrust and with spoilers deployed, and the Flight 1420 braking profile, the computer calculation showed that the airplane would depart the runway at 20 knots, 75 knots less than the airplane with no spoilers but with reverse thrust and braking. With constant reverse thrust, deployed spoilers, and the Flight 1420 braking profile, the computer calculation showed that the airplane could have stopped about 700 feet before the end of the runway. An animation illustrating the effects of spoilers and reverse thrust on stopping efficiency and controllability is available below:
Crosswinds

Photo copyright Diakoumakos Ilias - used with permission
During certification, the manufacturer is required to establish a crosswind value that will be used to determine operational capabilities. 14 CFR 25.237 requires that a crosswind value be established that is at least 20 knots, or 20% of the applicable stall speed, whichever is greater, but need not exceed 25 knots. The value of the demonstrated crosswind is required to be published in the FAA approved airplane flight manual (AFM), and if it is not considered to be a limit, the AFM may so state. Crosswind testing attempts to determine as high a value as possible. For example, a variety of airplane models in the operational fleet have demonstrated crosswind values that exceed 30 knots. However, it is rare that crosswind testing will actually demonstrate a limiting value. The determination of the crosswind value is largely a function of the winds available during the crosswind testing. It is not uncommon for a manufacturer to establish a value that complies with the applicable regulation, and then later conduct additional crosswind testing in order to demonstrate a higher value. The AFM contains a demonstrated crosswind value of 30 knots for the MD-80 series of airplanes, and further contains the statement that the 30-knot value is not considered to be a limit.

Photo copyright Juergen Trautwein - used with permission
Operationally, many carriers use the AFM-published demonstrated value as an operational limit, even though the actual limit has not been determined. Some operators may examine/analyze airplane geometry (wingtip/nacelle contact, crab angles, etc.) and calculate a value at which the airplane would encounter a geometry limit, thereby establishing company limits that may exceed the AFM-published value. In these cases, this practice has been determined to be acceptable, as an actual limit was not established by flight testing. It is not uncommon for operations to be conducted in crosswind values that exceed the demonstrated value published in the AFM.
American Airlines had adopted a company policy that restricted takeoff or landing operations to crosswind values greater than the demonstrated AFM values if certain runway or meteorological conditions were present. In this accident, the runway was known to be wet and/or slippery. In a wet runway situation, company policies limited the crosswind to 20 knots. The known crosswind, including gusts, during the approach exceeded 20 knots for an extended period. In this situation the NTSB concluded that the crew should have initiated a go-around and not landed.
Stabilized Approaches
In instrument weather conditions, a pilot must continuously assess instrument information throughout an approach to properly maneuver the aircraft (or monitor autopilot performance), and to decide on the proper course of action at the decision point (Decision Height or Minimum Decent Altitude/Missed Approach Point). Significant speed and configuration changes during an approach can seriously complicate tasks associated with aircraft control, increase the difficulty of properly evaluating an approach as it progresses, and complicate the decision of the proper action to take at the decision point.
Airplane handling and engine-response characteristics of most turbojet aircraft further complicate pilot tasks and decision-making during approach and landing operations. A pilot must begin formulating a decision concerning the probable success of an approach before reaching the decision point. The pilot's decision-making process requires the pilot to be able to determine displacements from the course or glidepath centerline, to mentally project the aircraft's three-dimensional flightpath by referring to flight instruments, and to then apply control inputs as necessary to achieve and maintain the desired approach path. This process is simplified by maintaining a stable approach speed, descent rate, vertical flightpath, and airplane configuration during the final stages of an approach.

Photo copyright Joao Toste - used with permission
Maintaining a stable speed, descent rate, vertical flightpath, and airplane configuration is a procedure commonly referred to as the stabilized approach concept. Operational experience has shown that the stabilized approach concept is essential for safe operations with turbojet aircraft, and it is strongly recommended for all other aircraft.
A stabilized approach for turbojet aircraft means that the aircraft must be in an approved landing configuration, must maintain the proper approach speed with the engines spooled up, and must be established on the proper flightpath before descending below the minimum "stabilized approach height" specified for the type of operation being conducted. These conditions must be maintained throughout the rest of the approach for it to be considered a stabilized approach. A stabilized approach must be established before descending below a minimum stabilized approach height of 1,000 feet above the airport or Touchdown Zone elevation during any straight-in instrument approach during instrument flight conditions.
The NTSB report noted that as the flight crew was maneuvering the airplane for landing, there were events that, individually, might not necessitate aborting an approach. These included a runway change because of a shifting wind; a failed visual approach to the newly assigned runway; the temporary inability of the airborne weather radar to show the weather conditions at the airport; the controller's report of the second part of the thunderstorm moving through the airport area; and the acceptance of a short approach near the outer marker because of the airplane's location in relation to the storm. However, these events, collectively, should have heightened the crewmembers' awareness that they might not be able to safely continue the approach. Thus, it would have been appropriate for the flight crew to have discussed specific options (holding, diverting to one of the two alternate airports, or performing a missed approach after the airplane was established on the final approach segment) in the event that the weather would necessitate aborting the approach later.
As the airplane intercepted the ILS final approach course for runway 4R, the flight crew entered an event-dependent, high workload phase of flight. Under normal conditions, tasks during this phase of flight include controlling and maneuvering the airplane, configuring the airplane to land, performing final landing checks, and evaluating the airplane's performance relative to the landing criteria. In this case, the flight crew's earlier decision to accept a short approach increased the crew's already high workload by compressing the amount of time that was available to accomplish required tasks.
The accident report noted that during the final approach, the flight crew had a significant amount of weather information that had to be simultaneously evaluated. This information included the controller's previous report of heavy rain at the airport with visibility less than 1 mile, the second windshear alert, a rapidly decreasing RVR, and several wind reports. Under these circumstances, some flight crews would have decided to abandon the approach, perform a go-around, or divert to another airport with more acceptable landing conditions.

on approach to land
Photo copyright Yo Tanaka - used with permission
The investigators further concluded that the flight crew then performed poorly, and they did not complete the second half of the before-landing checklist. Although the sound of the landing gear being operated was recorded by the CVR, there is no CVR evidence to indicate that the first officer verbalized this checklist item as "down, three green," as required. This call would have indicated that all three landing gear systems were in the down and locked position. Also, the captain commanded the 40° final landing flap configuration only after being queried by the first officer. The captain did not realize that he had not yet called for the flaps; as a result, this checklist item was performed late. In addition, there was no CVR evidence to indicate that the first officer called out that the spoiler lever was armed, checked the annunciator lights, and completed the before-landing checklist. Nor was it indicated that either pilot had armed the spoiler lever and considered the use of automatic breaking, rather than manual, in light of the deteriorating weather conditions.
The NTSB analysis indicated that the flight crew should have initiated a go-around during the final approach segment when a specific operational criterion was not met, that is, when the company's maximum crosswind component for conducting the landing was exceeded. The flight crewmembers' failure to establish the final landing flap configuration before reaching 1,000 feet above field level and their failure to maintain a normal rate of descent, under different circumstances, might not necessitate a go-around. However, the NTSB concluded that, because of the flight crew's failure to adequately prepare for the approach and the rapidly deteriorating weather conditions, the likelihood of safely completing the approach was decreasing, and the need to take a different course of action was progressively increasing. As a result, the flight crew should have abandoned the approach.
Runway Safety Areas and Non-frangible Structures
Runway 4R/22L was opened for aircraft operations in September 1991 and was built to abate noise over the communities located southeast of the airport. Runway 4R (oriented southwest to northeast) was intended to be used primarily for takeoffs, and runway 22L (oriented northeast to southwest) was intended to be used primarily for landings. There were site constraints on the design and construction of the runway, including the flood plain of a creek and rising terrain to the southwest and the flood plain of the Arkansas River to the northeast. The total length available for the runway and its associated safety areas was 8,650 feet. A runway length of 7,200 feet was needed, so 1,450 feet was available for the safety areas. The runway was designed so that a 1,000-foot safety area extended from the southwest (runway 22L) and a 450-foot safety area extended from the northeast (runway 4R).

Although the FAA's June 5, 1991, version of AC 150/5300-13 stated that the standard runway safety area was 1,000 feet, runway 4R/22L was exempt from this standard under the provisions of 14 CFR 139.309(a)(1), which allowed runways that had a safety area on December 31, 1987, to be maintained, as long as no reconstruction or significant expansion of the runway had begun after January 1, 1988. The NTSB noted in their report that, in this accident, an extra 550 feet at the departure end of runway 4R would not have prevented the airplane from departing the end of the runway or impacting the approach lighting system. However, the airplane's speed would have further decreased with an extra 550 feet at the end of the runway, resulting in a lower impact speed.
The FAA determined that the runway 22L approach lighting system at Little Rock, which is located in a flood plain area of the Arkansas River, could not be retrofitted to a frangible design because of the possibility that moving water, ice, and floating debris would affect the structural integrity of the system. The NTSB recognized the design limitations of this approach lighting system and acknowledged that, if the approach lighting system had been frangible, it is possible that the accident airplane would not have been stopped on the ground and would have gone into the Arkansas River. In this accident, the airplane's collision with the non-frangible approach lighting system (ALS) was the direct cause of the fatal blunt force trauma injuries sustained by the captain and the passengers in seats 3A and 8A and the destruction to the airplane on the left side of the fuselage.

In 1984, the NTSB issued Safety Recommendation A-84-36, which asked the FAA to "initiate research and development activities to establish the feasibility of submerged low-impact resistance support structures for airport facilities and promulgate a design standard if such structures are found to be practical." The FAA conducted research in this area with the National Institute of Standards and Technology. In October 1996, the FAA concluded that, with the current technology, any submerged low-impact frangible structure would most likely be destroyed by wave motion from small storms.
As a result of this accident, the NTSB issued Safety Recommendation No. A-01-68, which asked the FAA to conduct research activities to determine if recent technological advances would enable submerged low-impact structures and other non-frangible structures at airports to be converted to frangible ones. In 2002, and in response to this recommendation, the FAA undertook two initiatives to determine whether or not any advances in technology can be applied to submersible structures to make them more frangible, and to accelerate completion of the ALS Improvement Program which was initiated to replace non-frangible support structures with frangible land-mounted facilities. In 2003, the FAA reported that preliminary analysis of a typical fiberglass low-impact pole may be able to survive a certain level of high water flooding. The FAA responded, stating that if the use of a fiberglass low-impact pole is technically acceptable from a survival perspective, the potential operational stability and maintenance issues will be evaluated.
The NTSB requested that Engineered Arresting Systems Corporation of Lester, Pennsylvania, survey the accident area and provide information on any safety benefit that a soft-ground aircraft arresting system would have provided for Flight 1420 if such a system had been installed at the departure end of runway 4R. At the board's public hearing on this accident, a consultant for Engineered Arresting Systems discussed the company's Engineered Materials Arresting System (EMAS). The consultant described the EMAS as a passive system that decelerates an airplane when its wheels roll through a soft foamy material. He added that the system was designed to be compatible with all of the airplanes with which it would come in contact. The Engineered Arresting Systems Corporation's analysis included an EMAS that was designed to reflect the conditions that existed at the departure end of runway 4R. The total length of this EMAS was 402 feet.

- NTSB
In its report to the NTSB, Engineered Arresting Systems concluded that the benefit of an EMAS in this accident would have been limited by the airplane traveling partly outside the runway edges; thus, the airplane would not have been able to use the full length of the EMAS. The report also concluded that an EMAS would have reduced the speed of the airplane by 15 knots but would not have enabled the airplane to stop within runway 4R's runway safety area. In addition, the report concluded that, in this accident, an EMAS could have led to two landing gear failures because the loads exceeded the ultimate values determined by the airplane manufacturer.
On April 14, 1999, the FAA, the Little Rock Municipal Airport Commission, and the airport's tenants met at a joint planning conference to identify airport development needs for the next five years. According to the conference report, an arresting system for runway 4R/22L was identified as a recommended project for 2000. In the fall of 2000, an EMAS measuring 304 feet long and 200 feet wide was installed at the departure end of runway 4R.

Photo copyright William A. Jones - used with permission
Weather Information
Several sources of weather information were provided to Flight 1420's crew during a prefight briefing and in flight. According to the NTSB report, during a preflight briefing, the flight crew received a package of information that included reports, forecasts, and notices to airmen for the departure, destination, and alternate airports, and current in-flight weather advisories for the route.
One of the advisories was a thunderstorm SIGMET (significant meteorological condition) that described thunder storm activity over Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas, and Oklahoma. Other advisories in the preflight package included a brief of National Weather Service (NWS) Severe Weather Forecast Alert No. 357 and NWS Convective SIGMET No. 11C that indicated an area of severe thunderstorms with cloud tops above 45,000 feet, the possibility of hail up to two inches in diameter, and surface wind gusts to 70 knots over portions of Arkansas, including Little Rock. The preflight package also included the NWS North Little Rock Forecast Office's terminal aerodrome forecast for Little Rock and Little Rock's most recent Automated Surface Observing System (ASOS) observation. The terminal forecast and report indicated that all Little Rock runways were open, no rain, and no reports of braking action problems.
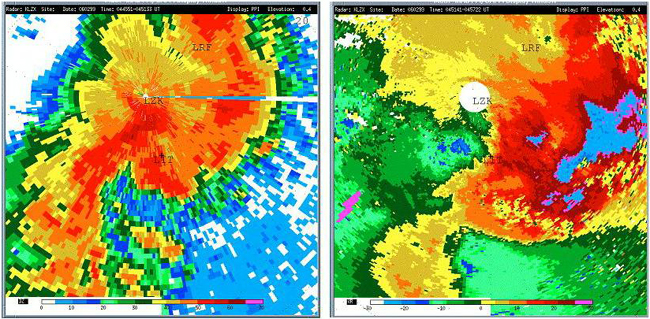
While in flight and en route to Little Rock, the flight crew received NWS Convective SIGMET No. 15C for an area of severe thunderstorms that included the Little Rock airport area. According to the NTSB report, the flight crew observed numerous lightning discharges as the airplane approached the city of Little Rock.
The ASOS records continuous information on wind speed and direction, cloud cover, temperature, precipitation, and visibility. The ASOS transmits an official meteorological aerodrome report (METAR) at 53 minutes past each hour and a special weather observation (SPECI) as conditions warrant. Such conditions include a wind shift, change in visibility, and change in ceiling (cloud cover or height). The system is prevented from issuing any reports for a six minute period, from 47 minutes past the hour to 53 minutes past the hour (know as the lockout period) so that the hourly observations can be prepared, edited and transmitted.
The NTSB investigation showed that just after 2347, about three minutes before the accident, a SPECI was canceled because it occurred during the lockout period. Further investigation revealed that at the time of the accident, a special observation was prepared by the ASOS, but not disseminated. That observation reported that the winds were from 290° at 16 knots gusting to 28 knots, visibility was 1.5 miles in thunderstorm and heavy rain and mist. In the remarks section, the report noted a shift in the winds, frequent lightning in the area, thunderstorms moving through the area, and, since the last hourly observation, 0.37 inch of precipitation had been recorded.
The NTSB also noted that by ten minutes after the accident, the ASOS recorded a rainfall of 1.09 inches. The ASOS hourly observation, three minutes after the accident, indicated the winds were 280° at 18 knots gusting to 26 knots and the visibility was one mile in thunderstorms and heavy rain and mist. By eight minutes after the accident, an ASOS SPECI reported winds from 290° at ten knots gusting to 76 knots; the winds varied from 210° to 030°; the visibility was 0.5 mile in thunderstorms, small hail, heavy rain; and a peak wind from 320° at 76 knots was measured about six minutes after the accident. In its report, the NTSB noted that, had Flight 1420 arrived at the Little Rock airport just a few minutes later than it did, it would have likely encountered a microburst on final approach. Microbursts can result in vertical and horizontal windshear that can be extremely hazardous to aircraft, especially at low altitudes. The NTSB expressed concern that Flight 1420 was operating in an environment that was conducive to microburst conditions.
In addition to the ASOS, the Little Rock airport is equipped with an FAA Type FA-10240 Low Level Windshear Alert System (LLWAS). The LLWAS uses six wind sensors at remote stations located around the airport to collect wind speed, wind direction, and gust data. LLWAS alerts are displayed in the Air Traffic Control Tower so that controllers can warn flight crews of potentially hazardous windshear conditions. During Flight 1420's approach to the airport, the controller on duty issued two windshear alerts.

U.S. Presidential Commission Formed
Throughout the 1980's and early 1990's, the rate of commercial aviation accidents in several major areas was not declining substantially, although many key safety initiatives had been introduced. In particular, several categories of accident areas, such as approach and landing related accidents and controlled flight into terrain (CFIT), continued to occur, and represented major areas of operational risks. Although the actual rates vary from year to year, for the last several decades, approximately half of all commercial accidents were observed to have occurred during approach and landing phases of flight. In response to the continued occurence of accidents in these categories and other major accidents, in the mid 1990's a U.S. Presidential Commission was formed for the purpose of assessing the efficacy of international commercial aviation safety and to identify areas for safety improvements in these major areas.

White House Commission on Safety and Security
Led by Vice President Al Gore, the White House Commission on Safety and Security issued its final report on February 12, 1997. This report challenged the FAA and industry to reduce the fatal accident rate by 80% over a ten-year period. In order for this to be achieved, the commission stressed the need for strong government-industry partnerships to support the aviation system of the future. Additionally, the National Civil Aviation Review Commission (NCARC) followed up the White House Report with a strong recommendation that the FAA and industry work together to develop a comprehensive, integrated strategic safety plan to implement the many existing safety recommendations. The Commission recommended that performance measures and milestones be developed to assess progress in meeting the safety goal. Further, the Commission advocated periodically reviewing priorities and monitoring progress made in achieving the overall safety goal.
View the White House Commission on Aviation Safety and Security - Final Report to President Clinton.
Commercial Aviation Safety Team (CAST)

"Results and Analysis" issued May 17, 2001

Recognizing that their safety work was complementary, in 1998 the FAA and aviation industry formed the Commercial Aviation Safety Team (CAST) with the goal to "develop methods to fully understand the chain of events leading to accidents." Original FAA, NASA and industry Commercial Aviation Safety Strategy groups were formed and tasked to, by using accident data, determine top safety focus areas. The objective of the CAST was to use data to develop an understanding of the best actions or interventions to take in order to prevent future accidents. As a part of the CAST activity, the Joint Safety Analysis Steering Committee (JSASC) was formed as the organizational body that would work together in these aviation safety areas. The scope of the work was to collaborate on identifying the highest risk safety areas through the analysis of past accident and incident data, charter joint teams of experts to develop methods to fully understand the chain of events leading to accidents, identify high-leverage interventions to address these safety areas, and remain focused on implementing these critical few high-leverage interventions in the identified areas. Approach and landing accidents represented one of the high-leverage areas identified by CAST where targeted intervention had the potential for substantial accident rate reductions.
The Joint Safety Implementation Team (JSIT) issued "Results and Analysis" on May 17, 2001. This report identifies approach and landing interventions and the overall effectiveness of these interventions in preventing commercial aviation accidents. The complete report is available at the following link: "Result and Analysis" by the Joint Safety Implementation Team (JSIT) - Approach and Landing.

Approach and Landing Accident Reduction (ALAR) Initiatives
Several initiatives were undertaken and intended to identify areas where safety interventions could be leveraged in order to reduce the rate of approach and landing accidents. These included the formation of three separate, but coordinated, task forces which developed specific training tools. These training tools, each with their own focus and style, include:
- Flight Safety Foundation ALAR Tool Kit, released in 1999, include a unique set of pilot briefing notes, videos, presentations, risk awareness check lists, and other information tools designed to reduce the risks of approach and landing accidents. Several subsequent revisions to the original 1999 version of the Tool Kit have since been released. Copies of the material in DVD format are available from the Flight Safety Foundation.
- FAA Advisory Circular AC 120-71A; Standard Operating Procedures for Flight Crew Deck Crewmembers. This advisory material stresses the importance of effective flight crew coordination and communication (CRM), and underscores the role stabilized approaches have in reducing the risk for approach and landing operations. The AC also references the FSF ALAR Tool Kit training tools.
- Air Transport Association (ATA) ALAR Training Guide. Development headed by the ATA, this guide includes training material intended to aid in the understanding of areas of risk during approach and landing operations, and to reduce the risk of accidents associated with this phase of flight.
A more comprehensive list of ALAR initiatives can be found in the "Resulting Regulations" section of this module.
Approach and Landing Accidents Continue to Occur
This accident is one in a series of approach and landing accidents that have occurred throughout commercial transport aviation. In 1998, the Flight Safety Foundation (FSF) published a task force report stating that between 1980 and 1998, an average of 17 fatal approach and landing accidents had occurred per year throughout the world involving both passenger and cargo operations. As a result of industry training and awareness efforts, approach and landing accidents have been reduced, but do continue to occur. For example, worldwide in 2008, there were eight approach and landing accidents, and in 2009 there were nine. The aviation community continues to focus resources on this category of accident through targeted training, conduct of ALAR related workshops, and issuance of training aids and advisory materials.

at Toronto, Canada, on Aug 2, 2005

at Kingston, Jamaica, on December 22, 2009

landing overrun at Chicago Midway Airport on December 8, 2005
The NTSB issued 36 findings relative to this accident, ranging from flight crew qualifications, flight crew performance, and crash and rescue performance, to FAA oversight of the airline. The complete text of the findings is available at the following link: (NTSB Findings).
The NTSB determined that the probable causes of this accident were:
"...the flight crew's failure to discontinue the approach when severe thunderstorms and their associated hazards to flight operations had moved into the airport area and the crew's failure to ensure that the spoilers had extended after touchdown.
"Contributing to the accident were the flight crew's (1) impaired performance resulting from fatigue and the situational stress associated with the intent to land under the circumstances, (2) continuation of the approach to a landing when the company's maximum crosswind component was exceeded, and (3) use of reverse thrust greater than 1.3 engine pressure ratio after landing."
The entire NTSB accident report is available at the following link: (Accident Report)
The NTSB issued 22 recommendations to the FAA and two recommendations to the National Weather Service, covering a wide range of subjects. The NTSB also reiterated two previous recommendations to the FAA that had been issued relative to other accidents. The complete text of the recommendations is available at the following link: (NTSB Recommendations)
14 CFR 25.125 Landing
14 CFR 25.237 Wind Velocities
14 CFR 121.651 Takeoff and landing weather minimums: IFR: All certificate holders.
The flight crew was flying the last segment of a long flight day, and according to the accident report, were fatigued and approaching the end of their allowed crew duty day. They were cognizant of their duty time limitations and did not want to exceed their allowable duty day. Further, due to the inclement weather, the approach induced a high crew workload and an associated level of stress. During the approach, the crew was concentrating on maintaining visual contact with the airport, and as a result, did not complete the landing checklist, resulting in a failure to arm the automatic spoiler system. It was also an American Airlines company procedure that, based on the location of the spoiler handle, the captain, seated on the left side of the flight deck, would arm the spoilers independent of which pilot was flying. In this accident, the captain was the pilot flying the airplane, and would have additionally been required to arm the spoilers during the high workload approach.
The investigation concluded that the situational stress associated with the approach and the difficulty in maintaining visual contact with the runway affected the crew's decision making, resulting in the continuation of an approach that should have been abandoned. The investigation determined there was no evidence that the crew, once deciding to expedite the landing, ever reevaluated that decision, which is considered consistent with the tendency for individuals to maintain their originally selected course of action until/unless they are presented with overwhelming evidence that the course of action is incorrect.
During the approach, the investigation concluded that there were several cues that indicated deteriorating weather, but neither crew member discussed initiating a go-around and/or considered anything other than the original plan of operation. The accident report stated that the crew's intention to expedite the landing diverted their attention away from other activities and affected their ability to properly assess the situation and make appropriate decisions. The NTSB concluded that the focus on expediting the landing contributed to their degraded performance.
- The automatic spoiler system was not armed prior to landing, and spoilers did not deploy (and were not manually deployed) following touchdown.
- Reverse thrust EPR exceeded the procedural maximum of 1.3 recommended for wet runways and resulted in rudder blanking and loss of directional control.
- Failure to execute a go-around when confronted with rapidly deteriorating weather in the vicinity of the airport, and multiple windshear alerts.
- The landing checklist would be properly executed and followed.
- The flight crew would adhere to the procedurally specified 1.3 EPR when using reverse thrust on a wet runway.
- A go-around or diversion to an alternate airport would be conducted when deteriorating weather conditions, including windshear alerts, are present.
United Airlines Flight 227, Salt Lake City, Utah, November 11, 1965
United Airlines Flight 227, a Boeing 727, crashed during an attempted landing at Salt Lake City Airport. The captain failed to recognize and arrest an excessive sink rate on final approach, resulting in a touchdown 335 feet short of the runway. The main landing gear sheared off, causing a breach in the fuselage, and the airplane caught fire while sliding down and off the right side of the runway. Failure of the main landing gear ruptured fuel lines and generator leads, causing the fire. The entire roof and cabin area forward of the fuselage breach was consumed by fire. Of the 85 passengers aboard, there were 43 fatalities. All six crew members survived. The Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) determined that the accident was survivable - none of the passengers sustained any traumatic injuries that would have precluded their escape. The 43 fatalities were attributed to the fire caused by the broken fuel line. The CAB also established that similar future events could not be ruled out, and that the airplane should be designed to have a higher degree of survivability in these types of events.
See accident module
Delta Airlines Flight 191, Dallas, Texas, August 2, 1985
Delta Airlines Flight 191, a Lockheed L-1011-385-1, crashed while approaching to land on runway 17L at Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport. The airplane entered a microburst, which the pilot was unable to traverse successfully. The airplane struck the ground more than a mile short of the runway, hit a car on the highway, struck two water tanks at the airport, and broke apart. The NTSB determined that the probable causes of this accident were the flight crew's decision to initiate and continue the approach into a cumulonimbus cloud, which the crew members observed to contain visible lightning; the lack of specific guidelines, procedures, and training for avoiding and escaping from low altitude windshear; and the lack of real-time windshear hazard information.
See accident module
USAir Flight 1016, Charlotte, North Carolina, July 2, 1994
USAir Flight 1016, a Douglas DC-9-31, collided with trees and a private residence after executing a missed approach to runway 18R at Charlotte/Douglas International Airport, Charlotte, North Carolina. At the time of the accident, adverse weather conditions existed over the airport and along the flight path. The NTSB determined that the probable causes of this accident were (1) the flight crew's decision to continue an approach into severe convective activity that was conducive to a microburst; (2) the flight crew's failure to recognize a windshear situation in a timely manner; (3) the flight crew's failure to establish and maintain the proper airplane attitude and thrust setting necessary to escape the windshear, and (4) the lack of real-time adverse weather and windshear hazard information dissemination from Air Traffic Control.
American Eagle Flight 4925, Jamaica, New York, May 8, 1999
American Eagle Flight 4925, a Saab 340B, overran the end of runway 4R at John F. Kennedy International Airport, Jamaica, New York. The captain flew the approach with excessive altitude, airspeed, and rate of descent, and he remained above the glideslope. The first officer failed to make required callout, including a missed approach callout. The NTSB determined that the probable cause of this accident was the captain's failure to perform a missed approach, as required by company procedures. Contributing to the cause of this accident were the captain's improper in-flight decisions and failure to comply with FAA regulations and company procedures, inadequate crew coordination, and fatigue.
There were no regulatory changes made as a result of this accident. The following paragraphs list the numerous changes to advisory material, FAA orders, and company procedures as a result of this accident:
Operational Procedures
In August 2000 the FAA issued Appendix 2 to AC 120-71, Standard Operating Procedures for Flightdeck Crewmembers. The AC includes stabilized approaches as one of the most important elements, and includes detailed criteria, with explicit guidance that a stabilized approach should be established no later than 1,000 feet above ground level in instrument meteorological conditions and no later than 500 feet above ground level in visual meteorological conditions. In October 2001 the FAA issued Flight Standards Bulletin for Air Transportation 01-02 (FSAT 01-12), Approach and Landing Accident Reduction (ALAR): Recommended Flight crew Training. The bulletin points to AC 120-71, the Flight Safety Foundation's Approach and Landing Accident Reduction (ALAR) Toolkit, and in an appendix, includes the ALAR Training Guide developed by a joint FAA-industry working group. An overview of the ALAR Tool Kit is available at the following link: (ALAR Tool Kit - Introduction to Briefing Guide) In 2008 FSAT 01-12 was superseded by FAA Information for Operators (InFO 08029), Approach and Landing Accident Reduction (ALAR): Recommended Flight crew Training. Further information and an overview of this InFO is available at: (InFO 08029 Supporting Information) (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-69).
In December 2002 the FAA issued a memorandum to all 14 CFR part 121 principal operations inspectors (POI) who have direct responsibility for MD-80 airplanes directing the POIs to call attention to the manufacturer's Flight crew Operating Manual recommended maximum of 1.3 engine pressure ration in reverse thrust during landings under wet or slippery runway conditions, except in an emergency where directional control can be sacrificed for decreased stopping distance. The FAA also directed the POIs to emphasize the importance of including the manufacturer's recommended maximum of 1.3 engine pressure ratio in the training program and flight manuals used by their respective operator's flight crews. In addition, the FAA directed POIs to call attention to November 2002 Boeing Long Beach Flight Operations Bulletin regarding thrust reversers, which reiterated information in the Boeing Long Beach MD-80 Flight Crew Operating Manual. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-51 and A-01-52)
In February 2003 the FAA amended Appendix 1 to Advisory Circular (AC) 120-71, Standard Operating Procedures for Flightdeck Crew Members, to include more explicit language regarding arming the automatic spoiler system. The language was qualified so it does not conflict with any operating procedures already approved by the FAA or recommended by the manufacturer for each specific airplane type and model. The language identifies, as a recommended standard operating procedure, the practice of dual crewmember confirmation that the spoilers have been armed before landing. Standard operating procedures appearing in AC 120-71, Appendix 1, are highly recommended by the FAA for inclusion in the manuals, checklists, and training programs used by U.S. airline pilots. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-49)
In February 2003 the FAA amended Appendix 1 to Advisory Circular (AC) 120-71, Standard Operating Procedures for Flightdeck Crew Members, to include more explicit language regarding callouts during ground spoiler deployment after landing. The language was qualified so it does not conflict with any operating procedures already approved by the FAA or recommended by the manufacturer for each specific airplane type and model. The language identifies, as a recommended standard operating procedure, a callout by the pilot not flying to verify that the spoilers have, in fact, deployed or have failed to deploy in response to automatic or manual activation after landing. Standard operating procedures appearing in AC 120-71, Appendix 1, are highly recommended by the FAA for inclusion in the manuals, checklists, and training programs used by U.S. airline pilots. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-50)
In February 2003 Boeing added a procedure in the Boeing MD-80 Flight Crew Operating Manual to have the pilot not flying make a callout at any time that a manufacturer's specific reverse power engine pressure ratio value is exceeded. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-53)
In June 2004 the FAA issued Notice N8400.68, Use of Autobrakes for Landing in Adverse Conditions. This notice was written for POIs; recommends the use of autobrakes for landings in adverse conditions caused by weather (for example, a wet or slippery runway or high crosswind); and directs POIs to convey the information in the notice to their respective certificate holders. This notice was cancelled in June 2005, and as the contained information was receiving special emphasis, the information contained therein was not incorporated into Order 8400.10, Air Transportation Operations Inspector's Handbook, but was dispositioned by other means. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-54)
An additional ALAR related operational initiative was produced in 2009 by the Flight Safety Foundation in cooperation with the International Air Transport Association (IATA). The Runway Excursion Risk Reduction Toolkit (RERR) was issued, focusing on the previous 14 years of landing accidents and showing there had been almost 30 excursions per year worldwide for commercial aircraft, which represented approximately 25% of all of the accidents that occurred during this period. This toolkit provides an in-depth analysis of runway excursion accident data; a compilation of significant risk factors, and provides recommendations for operators, pilots, airports, air traffic management, air traffic controllers and regulators to assist in addressing this challenge. The RERR Toolkit is available from the FSF.
Weather
In February 2004 the FAA updated the FAA's Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM) to provide information to pilots on Low Level Wind Shear Alert System (LLWAS) and alert data for controllers. LLWAS "Network Expansion," which is integrated with Terminal Doppler Weather Radar (TDWR), and LLWAS "Relocation/Sustainment" provide the capability of displaying microburst alerts, windshear alerts, and wind information oriented to the threshold or departure end of a runway. TDWR and Weather Systems Processors (WSP) are designed to detect windshear and microburst activity. The Integrated Terminal Weather System (ITWS) also provides detection and alerting for possible tornado activity, microbursts and windshear. The associated ribbon display allows controllers to read the displayed alert without any need for interpretation. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-61)
By July 2010 the FAA and the National Weather Service (NWS) implemented a short-term plan to ensure standardized, consistent, measurable and continuous operations. The Center Weather Service Units (CWSU) operate 16 hours per day, and the NWS Weather Forecast Office provides support for the remaining eight hours of each day. In addition, the CWSUs now provide finer resolution forecast information to Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON) facilities. Further improvements are being studied. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-58)
Air Traffic Procedures/Communication
In July 2002 the FAA issued a mandatory briefing to tower controllers that described the circumstances of the Little Rock MD-80 accident, including the interactions between the controller and ARFF crews. The mandatory briefing item is included in Air Traffic Bulletin, Issue 2002-1, Lessons Learned, and emphasizes that location information provided to ARFF crews should be as complete and specific as possible to minimize opportunities for confusion. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-62)
In May 2004 the FAA amended FAA Order 7110.65, Air Traffic Control, to require controllers to monitor the progress of airport rescue and firefighting crews responding to emergencies to ensure that the response is consistent with known location information. The change indicates that when workload permits, controllers should monitor the progress of emergency vehicles responding to a situation and, if necessary, provide available information to assist responders in finding the accident/incident scene. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-63)
In August 2004 the FAA amended FAA Order 7210.3, Facility Operation and Administration, to advise facility manager to meet with ARFF personnel on an annual basis to review the letter of agreement concerning local airport emergency services and the effectiveness of local procedures. A link to the June 2010 version of this order is available here: (Order 7210.3W) (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-64).
In addition to the above policy and advisory material changes, the FAA completed other changes to systems as a result of this accident. The following paragraphs summarize those changes:
In February 2011 the FAA successfully completed efforts to provide an automatic interface among Runway Visual Range (RVR) systems, the Automated Surface Observation System (ASOS), the Automated Weather Sensor System, and the Integrated Terminal Weather System. RVR data can now be accessed via either weather display system. The completion ends an improvement program begun in 2002. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-59)
By December 2010 the FAA completed an upgrade to the Teledyne RVR system that automatically archives data for 48 hours without human intervention. Other RVR systems produce data in a chart format with a retention requirement of 15 days. (Response to NTSB Recommendation A-01-60)
Runway Overrun Protection
On April 14, 1999, the FAA, the Little Rock Municipal Airport Commission, and the airport's tenants met at a joint planning conference to identify airport development needs for the next five years. According to the conference report, an arresting system for runway 4R/22L was identified as a recommended project for 2000. In the fall of 2000, an EMAS measuring 304 feet long and 200 feet wide was installed at the departure end of runway 4R.
Airplane Life Cycle:
- Operational
Accident Threat Categories:
- Landing / Takeoff Excursions
- Crew Resource Management
- Incorrect Piloting Technique
Groupings:
- Loss of Control
- Approach and Landing
- Automation
Accident Common Themes:
- Human Error
Human Error
During the approach, the flight crew concentrated on maintaining visual contact with the runway and did not complete the landing checklist. This resulted in a failure to arm the automatic spoilers, and, following touchdown, the spoilers did not deploy and were not deployed manually. This resulted in less effective braking and contributed to the eventual runway overrun. Further, for landing on a wet runway, both the manufacturer and the carrier specified a maximum EPR (thrust setting) of 1.3, in order to avoid rudder blanking and maintain directional control. Following touchdown, thrust reverse values exceeded 1.3, and further, the thrust values were slightly asymmetric, which could exaggerate directional control difficulties. The combination of crosswind, lack of spoiler deployment, and excessive reverse thrust settings combined to create a loss of control and the runway overrun. Finally, the investigation concluded that, given the deteriorating situation during the approach, the crew should have elected to perform a missed approach and go-around, which would have potentially avoided the accident.
Unstable Approach Related Accidents
United Airlines Flight 227, Salt Lake City, Utah, November 11, 1965
United Airlines Flight 227, a Boeing 727, crashed during an attempted landing at Salt Lake City Airport. The captain failed to recognize and arrest an excessive sink rate on final approach, resulting in a touchdown 335 feet short of the runway. The main landing gear sheared off, causing a breach in the fuselage. The airplane caught fire while sliding down and off the right side of the runway. Failure of the main landing gear ruptured fuel lines and generator leads, causing the fire. The entire roof and cabin area forward of the fuselage breach was consumed by fire. Of the 85 passengers aboard, there were 43 fatalities. All six crew members survived. The Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) determined that the accident was survivable - none of the passengers sustained any traumatic injuries that would have precluded their escape. The 43 fatalities were attributed to the fire caused by the broken fuel line. The CAB also established that similar future events could not be ruled out, and that the airplane should be designed to have a higher degree of survivability in these types of events.
See accident module
Weather related accidents
USAir Flight 1016, Charlotte, North Carolina, July 2, 1994
USAir Flight 1016, a Douglas DC-9-31, collided with trees and a private residence after executing a missed approach to runway 18R at Charlotte/Douglas International Airport, Charlotte, North Carolina. At the time of the accident, adverse weather conditions existed over the airport and along the flight path. The NTSB determined that the probable causes of this accident were (1) the flight crew's decision to continue an approach into severe convective activity that was conducive to a microburst; (2) the flight crew's failure to recognize a windshear situation in a timely manner; (3) the flight crew's failure to establish and maintain the proper airplane attitude and thrust setting necessary to escape the windshear, and (4) the lack of real-time adverse weather and windshear hazard information dissemination from Air Traffic Control.
Delta Airlines Flight 191, Dallas, Texas, August 2, 1985
Delta Airlines Flight 191, a Lockheed L-1011-385-1, crashed while approaching to land on runway 17L at Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport. The airplane entered a microburst, which the pilot was unable to traverse successfully. The airplane struck the ground more than a mile short of the runway, hit a car on the highway, struck two water tanks at the airport and broke apart. The NTSB determined that the probable causes of this accident were the flight crew's decision to initiate and continue the approach into a cumulonimbus cloud, which the crew members observed to contain visible lightning; the lack of specific guidelines, procedures, and training for avoiding and escaping from low altitude windshear; and the lack of real-time windshear hazard information.
See accident module
Fatigue related accidents
American Eagle Flight 4925, Jamaica, New York, May 8, 1999
American Eagle Flight 4925, a Saab 340B, overran the end of runway 4R at John F. Kennedy International Airport, Jamaica, New York. The captain flew the approach with excessive altitude, airspeed, and rate of descent and remained above the glideslope. The first officer failed to make required callout, including a missed approach callout. The NTSB determined that the probable cause of this accident was the captain's failure to perform a missed approach, as required by company procedures. Contributing to the cause of this accident were the captain's improper in-flight decisions and failure to comply with FAA regulations and company procedures, inadequate crew coordination, and fatigue.
Korean Air Flight 801, Nimitz Hill, Guam, August 6, 1977
Korean Air Flight 801, a Boeing 747-300, crashed at Nimitz Hill, Guam. The airplane had been cleared to land on runway 6L at Guam International Airport, Agana, Guam, and crashed into high terrain about three miles southwest of the airport. The NTSB determined that the probable cause of this accident was the captain's failure to adequately brief and execute the nonprecision approach and the flight crew's failure to effectively monitor and cross-check the captain's execution of the approach. Contributing to these failures were the captain's fatigue and Korean Air's inadequate flight crew training.
See accident module
Technical Related Lessons
If ground spoilers are installed as part of an airplane design, their deployment after touchdown, especially on wet or slippery runways, is necessary to achieve safe airplane stopping performance. (Threat Category: Landing/Takeoff Excursions)
- Safe landing and stopping performance are highly dependent on the airplane landing configuration and actuation of devices intended to aid in deceleration. Deployment of ground spoilers upon touchdown transfers the airplane's weight from the wings to the landing gear, allowing wheel brakes, the airplane's primary deceleration device, to develop the braking force necessary to achieve the required stopping performance. A post-accident study by the NTSB showed that if spoilers were deployed on touch down and without reverse thrust, Flight 1420 would have departed the end of the runway at about 20 knots rather than the actual value of about 100 knots. The NTSB study also showed that with ground spoilers deployed and constant reverse thrust, the airplane would have come to a stop well before the end of the runway.
Flight crew training programs should emphasize prompt initiation of a go-around, or rejected landing, when certain key conditions are identified during an approach or landing. Key conditions can include crosswinds of specific values; windshear alerts; failure to visually acquire the runway before, or at, decision height or minimum descent altitude; or deteriorating meteorological conditions. (Threat Category: Landing/Takeoff Excursions)
- In this accident, the runway was wet, and a crosswind was present that exceeded the American Airlines company 20-knot operational limit for wet runways. Weather was generally deteriorating, and the crew was attempting to expedite the approach. The NTSB concluded that the flight crew should have performed a go-around, delayed landing until the crosswind values had decreased within acceptable values and waited until the deteriorating weather had subsided. The combination of a high workload approach, excessive crosswinds for the runway conditions, deteriorating weather, and the lack of spoiler deployment to aid in deceleration, contributed to the loss of control on the ground as well as the runway excursion and overrun.
Common Theme Related Lessons
Task saturation, and fatigue can lead to significant degradation in flight crew performance. Expedited approaches should not be accepted in night or in instrument meteorological conditions without determining if sufficient time is available to complete all critical tasks. (Common Theme: Human Error)
- An operator either adopts an airplane manufacturer's recommended procedures or develops equivalent procedures to operate the airplane safely. The procedures are designed to assist the crew in properly configuring each of the aircraft's systems critical for phases of flight such as takeoff and landing. On the accident flight, the flight crew was confronted with several events that increased their workload: a runway change due to shifting winds, a failed visual approach to the newly assigned runway, and acceptance of a short approach due to the airplane's location relative to the storm. The NTSB report said that these factors compressed the time available for the crew to accomplish the required tasks. The crew did not complete the second half of the before landing checklist. The captain did not realize that he had not called for the final landing flap configuration, and there was no CVR evidence to indicate that the first officer called out that the spoilers were armed. Consequently, when the airplane landed, the ground spoilers did not deploy.
The investigation also concluded that crew fatigue may have played a role in the crew's deteriorated decision making. Post-accident investigation and assessment of the role played by fatigue in various accidents, led investigators to conclude that the flight crew degraded performance was consistent with known effects of fatigue.
