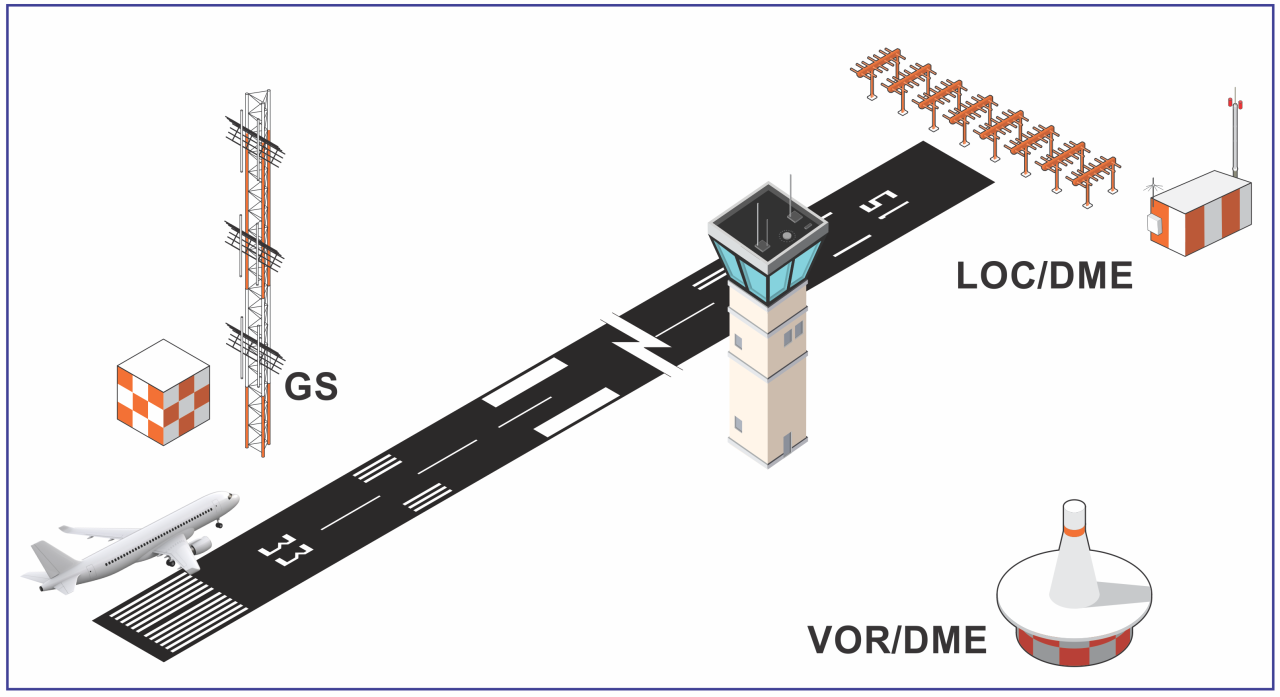
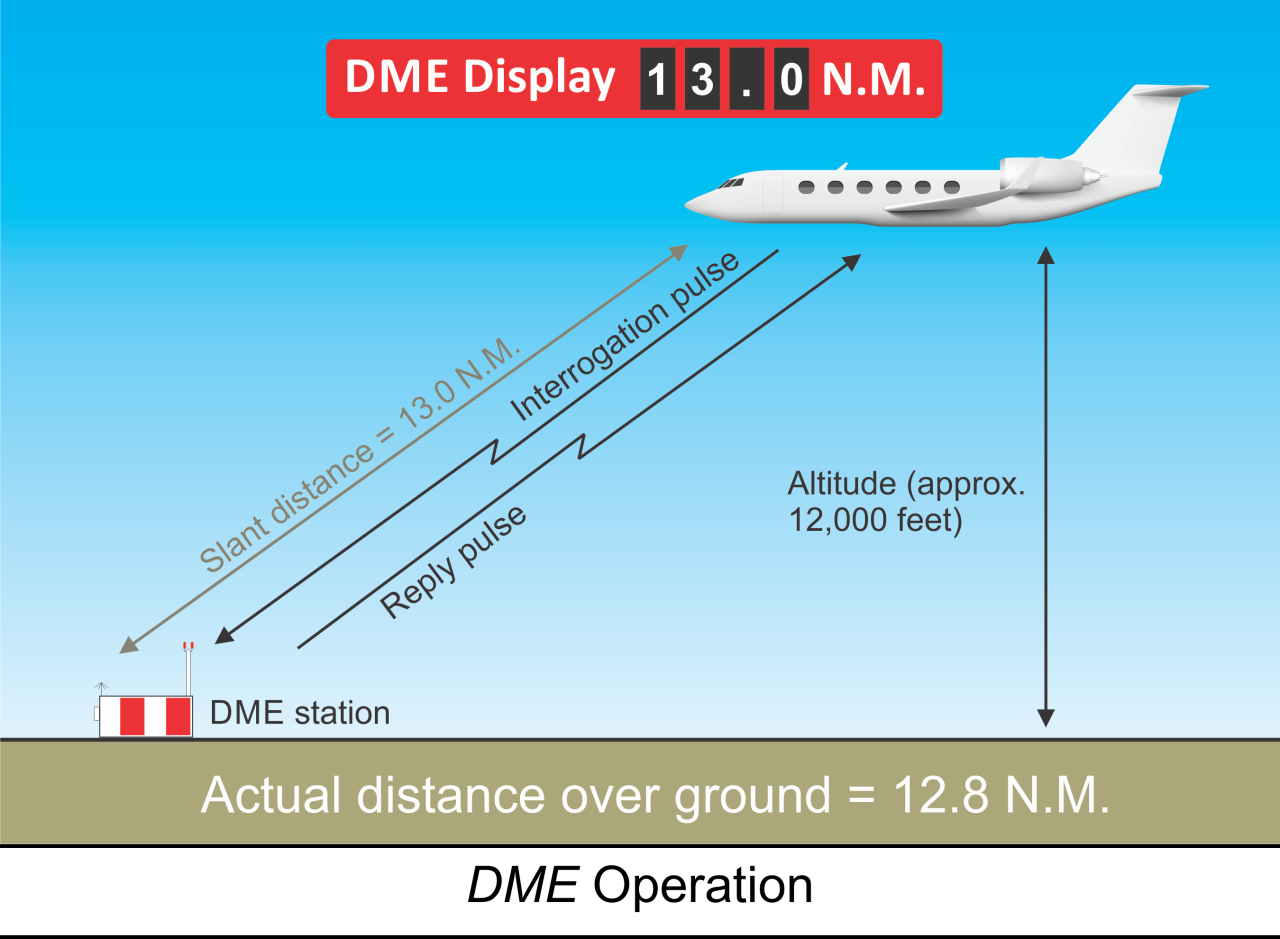
DME is used for measuring the slant range between the aircraft and facility. It operates in the 960 – 1215 MHz band. The DME avionics in aircraft sends a pulse signal to the ground based DME, which responds with an answer pulse signal. The receiver in the aircraft measures the time delay between the sent and received pulses and calculates the slant range distance. There is no azimuth information, only distance.
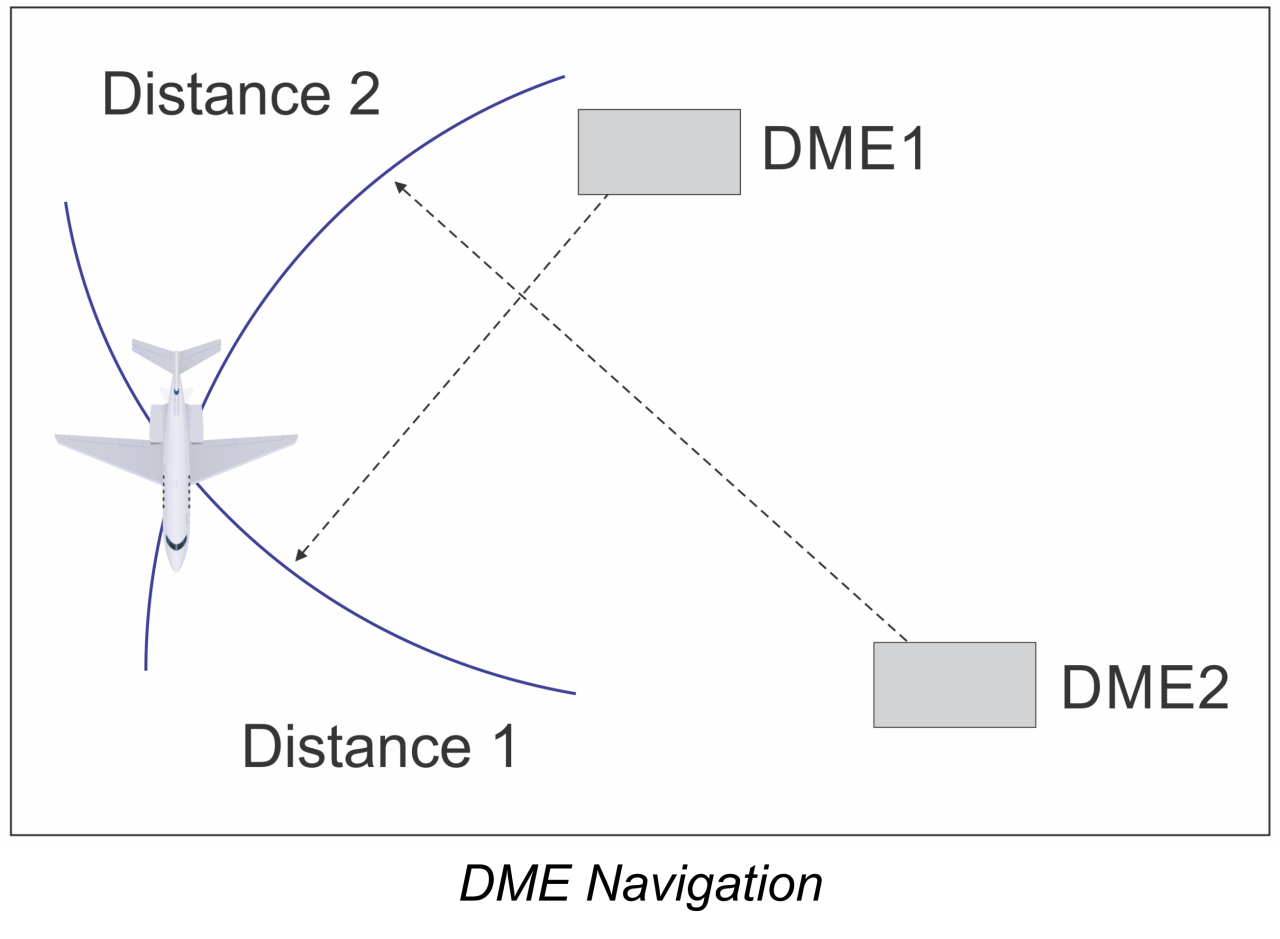
Low-Power DMEs (LPDME) transmit 100 watts of power and are used for approach navigation, usually associated with an Instrument Landing System (ILS) for terminal navigation. High-Power DMEs (HPDME) transmit 1,000-watts of power and are usually collocated with Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range (VOR) to support en-route navigation. HPDMEs collocated with VHF Omnidirectional Range (VOR)s allow aircraft to determine location on an airway during the en-route phase of flight. Aircraft equipped with scanning DME receivers can determine range and location using multiple HPDMEs. This method, referred to as DME/DME navigation enables flying Area Navigation (RNAV) en-route Instrument Flight Procedures (IFP).
The NEXTGEN DME program sustains HPDMEs required for RNAV en-route procedures as a resilient backup for GPS navigation.

Last updated: