NWP Products
NextGen Weather Processor (NWP) products are divided into four main categories:
- Mosaic products combine similar products from multiple data sources.
- Analysis products implement algorithms using past and current data to generate products that depict current weather conditions.
- Predictive products implement algorithms using past and current products as well as NOAA numerical weather forecasts to generate products that predict future flight-impacting conditions.
- Translation products convert weather information into weather avoidance products.
Mosaic Products
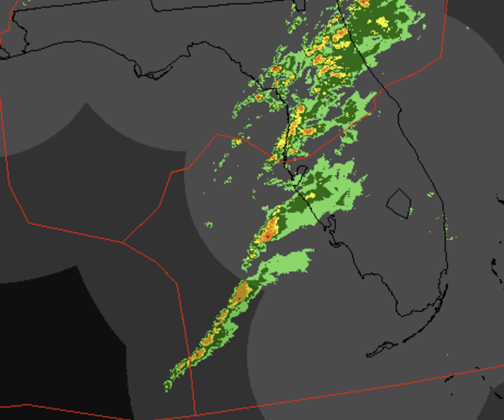
Air traffic controllers must be confident the weather they see on their scopes matches what the pilot is encountering in the air. NWP's radar volume products update rapidly, and its multi-radar mosaics are time-synchronized. For the first time, controllers' scopes will show storms without distortion in the correct location at all times. In addition to the contiguous United States (CONUS), NWP's extended coverage domain includes areas covered by radars in Canada and Puerto Rico. Domains for Alaska, Hawaii and Guam are included as well.
Next Generation Radar, Terminal Doppler Weather Radar, and Canadian Radars
- Precipitation
- Composite reflectivity (flexible 1000-foot layers)
- Base reflectivity
- Echo tops (Levels 1-6)
GOES Satellite
- Combined east/west visible and infrared
Analysis Products
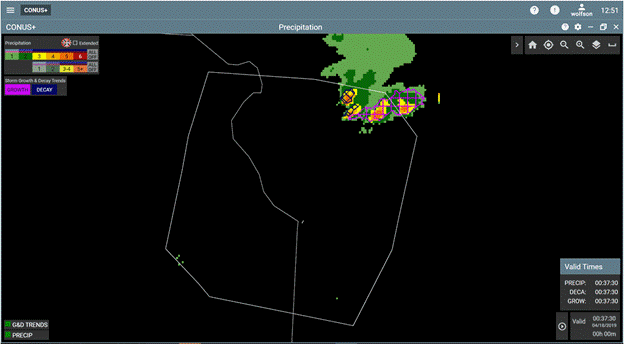
NWP's aviation-specific analysis products, based primarily on Doppler radar data, are important to pilots, controllers and traffic flow managers. The NWP growth and decay trends product, updating every 25 seconds, highlights rapidly growing storms that are unsafe to fly over—even when storm intensity is still weak. As shown on the NextGen Weather Aviation Weather Display, magenta cross-hatch areas (center) indicate growth areas, and dark blue cross-hatch areas (upper right) depict decay trend areas.
Storm Information
- Storm motion vectors
- Storm extrapolated position
- Growth and decay trends
- Echo top tags, hail
- Lightning, mesocyclone
Wind Shear Safety
- Tornado detections
Terminal Winds
- Wind profiles and 3-D grids
Predictive Products
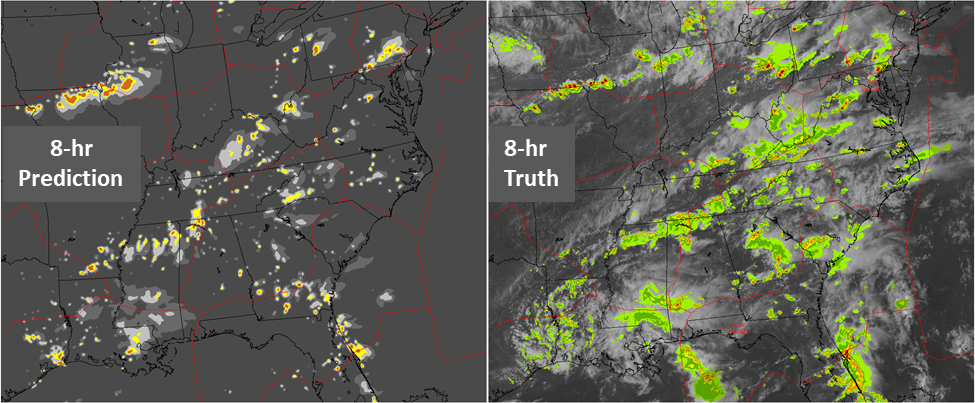
Aviation users have asked for "radar-forward" predictive products that appear to extend a loop of past radar detections into the future. The NWP generates this look-ahead out to 8 hours for precipitation (shown above) and echo tops. An accuracy score is provided for 0-2 hour lead times, and a confidence metric is provided for lead times out to 8 hours. These indicators help users gauge storm likelihood and strategies for developing traffic management initiatives. Pass-through products from the National Weather Service such as icing, turbulence and fronts are also integrated for display.
0-8 Hour
- Precipitation
- Precipitation phase (snow - mix - rain)
- Echo tops
- Confidence
0-2 Hour
- Accuracy Scores
- Fronts (time-aligned)
Translation Products
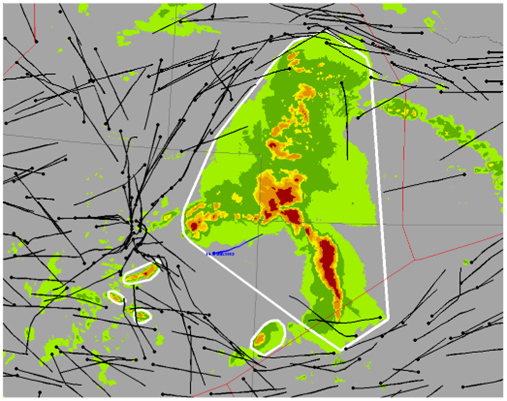
NWP radar mosaics and predictive products are translated into altitude-dependent airspace impact areas, with a quantitative probability assessment of pilot deviation likelihood called Convective Weather Avoidance Fields. This high-resolution information is precisely what is needed to predict route blockage and airspace capacity impacts up to 8 hours in advance. The Convective Weather Avoidance Polygons provide “fly vs no-fly” zones for display, essentially predictions of flow constrained areas that pilots will seek to avoid.
0-8 Hour
- Convective Weather
Avoidance Fields (CWAF) - Convective Weather
Avoidance Polygons (CWAP)
0-2 Hour
- CWAF for Route Availability Planning Tool
and Arrival Route Status and Impact
