What are Dangerous Goods?
The thought rarely crosses our minds, but many of the goods we use on a regular basis pose dangers to the aircraft. For example, lithium batteries, dry ice and aerosol whipped cream are dangerous goods. These products may seem harmless; however, when transported by air they can be very dangerous. Vibrations, static electricity, temperature and pressure variations can cause items to leak, generate toxic fumes, start a fire, or even explode if these products are not handled properly.
A dangerous good (also known as hazardous material or hazmat) is any substance or material capable of posing an unreasonable risk to health, safety, and property when transported in commerce. Identifying dangerous goods is the first step to reduce the risks posed by the product with proper packaging, communication, handling, and stowage. This is an important aspect of cargo safety.
The United States Department of Transportation has a system of classifying dangerous goods based on the product's specific chemical and physical properties. A good starting point for determining if your product might be dangerous is by obtaining a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) from the manufacturer and checking the "Transportation Information." This can provide valuable information on the transport risks related to your materials.
Common Dangerous Goods Examples
Safety Data Sheets
Dangerous Goods Hazard Classes
The Department of Transportation categorizes dangerous goods into nine hazard classes that describe different types of risks. For example, Class 3 includes flammable liquids and Class 8 includes corrosive materials. The table below provides awareness of how these hazard classes can translate to common materials that are considered regulated dangerous goods for transportation. This list is not exhaustive and is for general awareness purposes only. Always confirm the hazard classification of your product before shipping. The Department of Transportation's Hazardous Materials Table provides additional details about specific dangerous goods.
| DOT Hazard Class | DOT Hazard Class Label | Common Examples | Example Products |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Divisions 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, and 1.6 |
 |
Ammunition, fireworks |   |
|
Divisions 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 |
   |
Aerosols (e.g., spray paint, household cleaners, hair products, deodorants, cosmetics, cooking sprays), lighters, butane cans, oxygen, CO2 cartridges, flammable gas powered machinery & equipment, fire extinguishers |     |
| Class 3, Flammable Liquid |  |
Paints, paint-related materials (e.g., paint thinners, stains, sealants, coatings), extracts/flavoring liquids, perfumes/fragrances, adhesives, hand sanitizers, flammable liquid powered machinery/equipment |    |
|
Class 4, Flammable Solid, Spontaneously Combustible, and Dangerous When Wet Divisions 4.1, 4.2, and 4.3 |
   |
Strike-anywhere matches |  |
|
Class 5, Oxidizer, Organic Peroxide Divisions 5.1 and 5.2 |
  |
Oxygen generators, cleaners/chemicals (such as higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide), adhesive activators, curing products, resin kits |   |
|
Class 6, Poison (Toxic), Poison Inhalation Hazard, Infectious Substance Divisions 6.1 and 6.2 |
  |
Insecticides/pesticides, regulated medical waste, infectious substances |
  |
| Class 7, Radioactive |  |
Radiopharmaceuticals, radioactive sources (such as those found in certain smoke detectors and medical devices) |  |
| Class 8, Corrosive |  |
Cleaners and chemicals (e.g., swimming pool supplies like chlorine), many acids (e.g., sulfuric, hydrochloric, potassium/sodium hydroxide), wet batteries and battery acid, paint strippers |    |
| Class 9, Miscellaneous Hazardous Materials and Lithium Batteries | 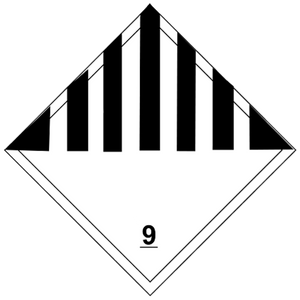  |
Lithium batteries, electronics containing lithium batteries (including cargo tracking devices), dry ice, machinery/equipment containing miscellaneous hazardous materials integral components (e.g. compressed gas accumulators, safety devices) |    |
