Advanced Air Mobility Infrastructure
Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) aircraft is an umbrella term for aircraft that are typically highly automated, electrically powered, and have vertical take-off and landing capability. Many of these aircraft fall into the powered-lift category are often referred to as air taxis. AAM aircraft could also be used to transport cargo and passengers, help with firefighting, and provide search and rescue operations.
While initial AAM operations will leverage existing infrastructure like airports and heliports (with modifications), new facilities, such as vertiports and vertistops – specialized areas for vertical takeoff and landing – will also accommodate these growing operations.
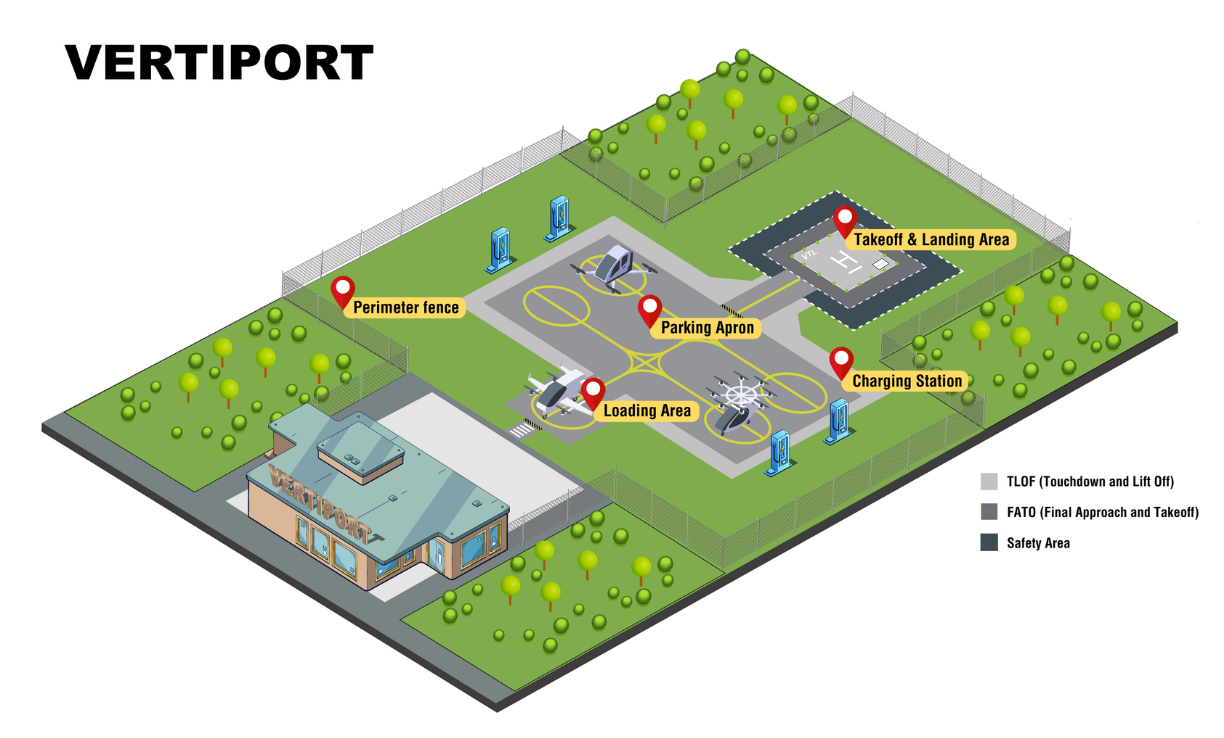
A vertiport is an area of land, water, or a structure used, or intended to be used, to support the landing, takeoff, taxiing, parking, and storage of powered-lift aircraft or other aircraft that vertiport design and performance standards established by the Administrator can accommodate. (FAA Reauthorization Act of 2024, Subtitle B – Advanced Air Mobility, Section 951(5))
Vertiports are a type of heliport.
Vertiport Design
The FAA’s Office of Airports (ARP), with the assistance of the FAA’s Airport Technology Research and Development Branch (ATRD) at the FAA William J. Hughes Technical Center, has developed and will continue to update design and safety standards for vertiports.
- Engineering Brief (EB) 105A, Vertiport Design, Supplemental Guidance to Advisory Circular 150/5390-2D, Heliport Design
The EB is specific to eVTOL aircraft with a pilot onboard, operating in Visual Meteorological Conditions (VMC), and a maximum takeoff weight of 12,500 pounds.- EB 105A, Vertiports Industry Day, January 14, 2025
The FAA provided an overview of the final EB update, discussed some critical changes made to the document, and answered audience questions.
- EB 105A, Vertiports Industry Day, January 14, 2025
Vertiport Construction
Existing FAA regulations on the development of new takeoff and landing facilities also apply to AAM infrastructure. These regulations ensure FAA has the information needed to evaluate the safety of a proposed takeoff and landing facility, its surrounding area, and any impacts to the existing National Airspace System.
- 14 CFR Part 157, “Notice of Construction, Alteration, Activation, and Deactivation of Airports” (Part 157)
Requirements for notifying the FAA about the proposed construction of a new vertiport, including updating the Airport Master Record within 15 days of completion of any airport/vertiport project. The Airport Data and Information Portal (ADIP) is available for airport/vertiport submissions. - 14 CFR Part 77, "Safe, Efficient Use and Preservation of the Navigable Airspace" (Part 77)
Standards governing aeronautical studies
Electric Charging Stations
Many AAM aircraft manufacturers are exploring electric batteries as an alternative fuel source, which will require access to charging infrastructure on or near an airport or vertiport. Facility owners and operators will need to carefully consider the siting and operations of charging stations as part of their overall site planning.
Interim Recommendations
While standards and guidance are being developed, ARP recommends early engagement and coordination with a local Airports District Office (ADO) or Regional Office (RO) for planned projects at federally obligated airports.
Key planning considerations include airport layout plan updates and airspace reviews toward evaluating compatibility with existing or planned infrastructure.
Hydrogen Fuel Storage
The FAA has also seen growing interest in using hydrogen as an alternative fuel source. The FAA and NREL have begun researching hydrogen fuel storage at airports and will provide guidance to industry once the appropriate data has been collected and analyzed.
Airport AAM Contacts
For general questions about vertiports and vertiports design standards/guidance, please send your questions to vertiports@faa.gov.
For questions specific to airport/vertiport sites, please reach out to the appropriate Regional Airport AAM Contact:
- Alaskan
- Central (IA, KS, MO, NE)
- Eastern (DC, DE, MD, NJ, NY, PA, VA, WV)
- Great Lakes (IL, IN, MI, MN, ND, OH, SD, WI)
- New England (CT, ME, MA, NH, RI, VT)
- Northwest Mountain (CO, ID, MT, OR, UT, WA, WY)
- Southern (AL, FL, GA, KY, MS, NC, PR, SC, TN, VI)
- Southwest (AR, LA, NM, OK, TX)
- Western-Pacific (AZ, CA, HI, NV, GU, AS, MH)
Related Links
General
Airport Cooperative Research Program (ACRP) Reports
- Airport-Centric Advanced Air Mobility Market Study
- Preparing Your Airport for Electric Aircraft and Hydrogen Technologies
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Federally obligated airports must update their ALP to include AAM infrastructure such as charging stations or on-airport vertiports.
For heliport facilities that serve single, tandem (front and rear), or dual (side by side) rotor helicopters and intend to accommodate emerging VTOL aircraft, the proponent should follow the recommendations in EB 105A and mark the facility as a vertiport unless the facility is built with a load bearing area (LBA) that meets the sizing requirements in EB 105A, incorporates an appropriately sized Downwash Caution Area (DCA) and adheres to the site safety elements for VTOL aircraft.
Yes. A new Form 7480-1, “Notice for Construction, Alteration and Deactivation of Airports”, is required to ensure that all appropriate FAA offices have an opportunity to review the proposal. Conversions may result in different levels of operations and flight profiles that would necessitate having other FAA offices evaluate potential impacts to the National Airspace System (NAS). For federally obligated airports, a proposed change from a heliport to a vertiport is initiated through an ALP update.
The pathway to dual-use facilities that serve both helicopters and powered-lift aircraft will be governed by helicopter and powered-lift aircraft performance. The FAA is conducting research to develop performance standards that will provide a framework for classification of landing facilities. For the time being, vertiports may accommodate helicopters that fit within the controlling dimension and maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) of the design VTOL.
In order to determine potential impacts of a proposed vertiport to the NAS, which includes other airports, the vertiport proposal must be reviewed through the FAA’s Obstruction Evaluation/ Airport Airspace Analysis (OE/AAA) system. FAA offices responsible for evaluating proposals for potential impacts to the NAS receive notice when sponsors submit proposals to the OE/AAA system.
When a Form 7480-1 is submitted for a new vertiport, the FAA will conduct an airspace review and issue a determination on the proposal’s impact to the safe and efficient use of navigable airspace and with respect to the safety of persons and property on the ground. In this case, the FAA issues a determination, not an approval. This determination will generally take up to 90 days. (See note below.)
When a FAA Form 7460-1, “Notice of Proposed Construction or Alteration”, is submitted for the construction of a vertiport on a federally obligated airport, the FAA must first assess if the vertiport is reflected on an FAA-approved ALP. If not shown, the sponsor will have to update the ALP before the airspace review can begin. Once the ALP is updated, the review will generally take up to 90 days. (See note below.) An environmental review under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) will also be necessary for this action.
NOTE: While FAA’s goal is to conduct an airspace review and issue a final airspace determination within 90 working days, vertiport cases are taking longer because they are novel facilities and lack certificated aircraft. As the FAA continues to develop policies and standards to address the integration of these aircraft, the Office of Airports will support regional and field offices in their reviews of early facility proposals. Please continue working closely with your local RO/ADO on AAM infrastructure proposals.
For more information about charging stations, vertiports, and related infrastructure, contact your local RO/ADO. For general inquiries about AAM, contact your local Regional Administrator.
No. Sponsor-furnished charging stations should be available to all aeronautical users (non-exclusive). This is similar to traditional aircraft self-fueling availability, which is protected by the grant assurances. Exclusive-use AAM leased property with proprietary charging stations are not considered an exclusive-right. Like other air carriers, AAM users have the right to self-fuel and self-maintain their aircraft.
Not currently. There is growing interest in the use of hydrogen and hydrogen fuel cells for powering traditional and new aircraft, which requires the need for hydrogen storage at airports. The FAA’s ATRD Branch, in collaboration with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, is currently researching hydrogen infrastructure standards. In the meantime, federally obligated airports interested in siting hydrogen storage on their airport must contact their local RO/ADO. An updated airport layout plan (ALP) may be needed. These projects will be reviewed on a case-by-case basis while ARP works to develop national guidance for hydrogen storage on airports.
Yes, for federally obligated airports and public-use, non-federally obligated airports. To ensure there are no impacts to Part 77 surfaces, identify aircraft charging stations in the OE/AAA system for both permanent and temporary construction. Refer to AC 150/5300-20, Submission of On-Airport Proposals for Aeronautical Study, on how to file notice to the FAA.
Not currently. Please refer to EB 105A for suggested charging station standards while final siting criteria is still being developed. Carefully consider whether the charging station location could limit or impact operations.
